| A | B |
|---|
| Asthenosphere | Is the ductile part of the earth just below the lithosphere, including the lower mantle. The asthenosphere is about 180 km thick., 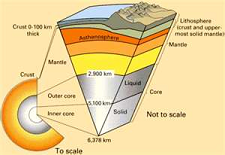 |
| Climate | The general character of the weather in an area over many years.,  |
| Day | The interval of light between two successive nights,  |
| Evaporation | The process that occurs when vaporization takes place only on the surface of liquid.,  |
| Geologic Time | The period of time covering the formation and development of the Earth, from about 4.6 billion years ago to today,  |
| Igneous Rock | A rock formed by the cooling and hardening of hot, liquid rock material,  |
| Main Sequence | Of or dealing with a major group of stars forming a band stretching from upper left to lower right on a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram when being plotted by luminosity and surface temperature., 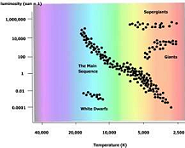 |
| Natural Gas | A gaseous fossil fuel found trapped deep underground, often with oil deposits.,  |
| Photovoltaic Cell | A photocell in which an electromotive force is generated by a photovoltaic effect., 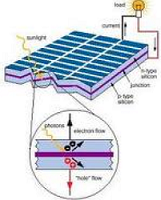 |
| Principle of Superposition | The principle that in a series of stratified sedimentary rocks the lowest stratum is the oldest., 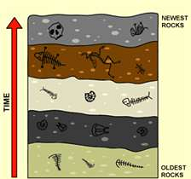 |
| Rotation | The act or process of turning around a center or an axis., 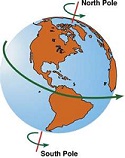 |
| Solar Energy | Energy from the sun, 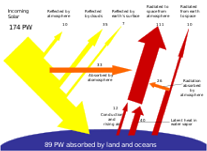 |
| Supernova | An explosive that breaks apart a massive star.,  |
| Tsunami | A surface wave on the ocean caused by an underwater earthquake, 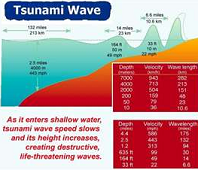 |
| Water Table | Upper surface of groundwater below which soil is saturated with water that fills all voids and interstices, and where the pressure of water in the soil equals the atmospheric pressure., 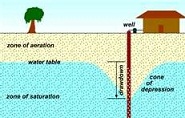 |