| A | B |
|---|
| Anaerobes | An organism that can live in the absence of atmospheric oxygen.,  |
| Biosphere | The regions of the surface and atmosphere of the Earth (or other planet) where living organisms exist,  |
| Cephalization | Is the process in animals by which nervous and sensory tissues become concentrated in the "head." The evolution of a head allows scientists to distinguish between the head end, or anterior end of an animal's body, and the opposite end, the posterior.,  |
| Cornea | The transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber., 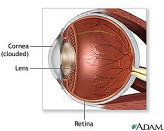 |
| Eardrum | Is a thin membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear., 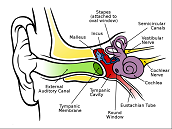 |
| Extinction | The act or process of becoming extinct; a coming to an end or dying out.,  |
| Golgi Body | An organelle, consisting of layers of flattened sacs, that takes up and processes secretory and synthetic products from the endoplasmic reticulum and then either releases the finished products into various parts of the cell cytoplasm or secretes them to the outside of the cell., 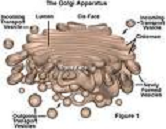 |
| Hypertonic | Noting a solution of higher osmotic pressure than another solution with which it is compared ( opposed to hypotonic)., 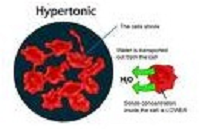 |
| Lymph | A fluid that bathes all body cells and acts as a go-between in the exchange of materials between the blood and the cells., 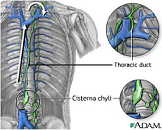 |
| Monocot | A group of flowering plants belonging to the class Liliopsida (or Monocotyledonae) of Angiospermae (angiosperms), characterized by having only one cotyledon in the seed and an endogenous manner of growth., 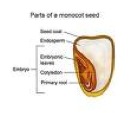 |
| Nutrient | A substance that provides energy or raw materials that the body needs in order to grow, repair worn parts or function properly, 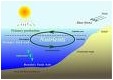 |
| Phylum | One of the major divisions of the kingdoms of living things, 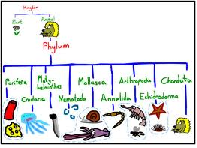 |
| Response | The reaction of a living thing to a change in its environment,  |
| Sterilization | The killing of all microorganisms in an area, usually by heating.,  |
| Trophic | Of or pertaining to nutrition, 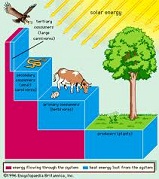 |