| A | B |
|---|
| Analogous | Similar in function, but not evolved from similar organs, as the wings of a bee and those of a hummingbird, 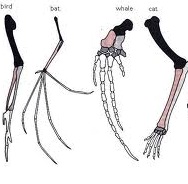 |
| Blood | A liquid tissue that conatins white and red blood cells, and platelets, and also carries dissolved gases, nutrients, hormones, and wastes, 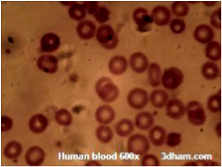 |
| Chlorophyll | Is the molecule that absorbs sunlight and uses its energy to synthesis carbohydrates from CO2 and water.,  |
| Cuticle | The outermost layer of the skin of vertebrates; epidermis,  |
| Echolocation | The use of reflection of sound waves to negative and to locate prey., 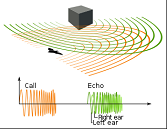 |
| Facilitated Diffusion | (Also known as facilitated transport or passive-mediated transport)Is a process of passive transport, facilitated by integral proteins., 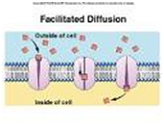 |
| Golgi Complex | A membranous complex of vesicles, vacuoles, and flattened sacs in the cytoplasm of most cells involved in intracellular secretion and transport, 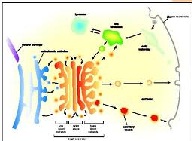 |
| Hypotonic | Refers to a solution with a comparatively lower concentration of solutes compared to another, 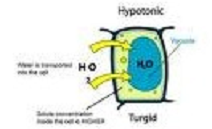 |
| Lymph Vessels | A tubes in which waste-laden lymph in collected and returned to the bloodstreams., 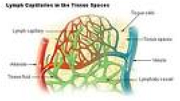 |
| Multicellular | Having or consisting of many cells or more than one cell to perform all vital functions.,  |
| NUTRIENT CYCLE | In ecology and Earth science, a biogeochemical cycle or nutrient cycle is a pathway by which a chemical element, 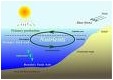 |
| Plankton | The collection of small or microscopic organisms, including algae and protozoans, that float or drift in great numbers in fresh or salt water, especially at or near the surface, and serve as food for fish and other larger organisms.,  |
| Retina | The layer of cells that lines the inside of the eyeball., 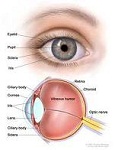 |
| Stimulus | A change in the environment that causes an organism to react in some way, 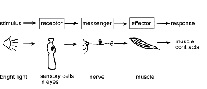 |
| Unicellular | Is an organism consisting of only one cell, 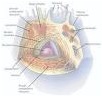 |