| A | B |
|---|
| Anaphase | The stage of mitosis and meiosis in which the chromosomes move to opposite ends of the nuclear spindle., 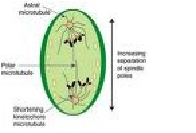 |
| Blood Vessels | Tubes through which the blood flows, 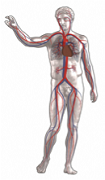 |
| Chloroplast | A plastid containing chlorophyll, 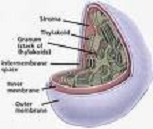 |
| Cytoplasm | The protoplasm outside the nucleus of a cell., 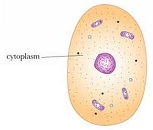 |
| Ecological Succession | The natural process by which one community of living things is replaced by another community, until a stable climax community appears.,  |
| Farsightedness | Condition that causes a person to see nearby objects as blurry., 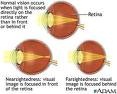 |
| Guanine | A purine base, C5H5N5O, that is a fundamental constituent of DNA and RNA, in which it forms base pairs with cytosine., 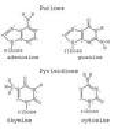 |
| Infectious Disease | A disease caused by microorganisms that can be transmitted from one individual to another. |
| Lysosomes | Are cellular organelles which contain acid hydrolase enzymes to break up waste materials and cellular debris., 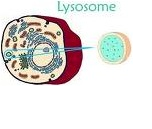 |
| Muscles | A tissue composed of fibers capable of contracting to effect bodily movement.,  |
| OMNIVORE | Animal that eats both plants and meat,  |
| Polypeptide | A chain of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds and having a molecular weight of up to about 10,000., 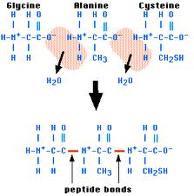 |
| Retroviruses | Are viruses that incorporate their genetic code (RNA) into host cells through means of enzymes called reverse transcriptase, which creates DNA from RNA (as opposed to the normal flow, RNA from DNA), and integrase, which makes the virus part of the cell's own genetic information., 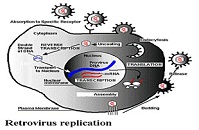 |
| Stomata | Microscopic openings on the undersurface of leaves that allow gas exchange and water evaporation from inside the leaf.,  |
| Uracil | A colourless, crystalline organic compound of the pyrimidine family that occurs as a component of ribonucleic acid (RNA), a molecule involved in the transmission of hereditary characteristics, 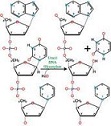 |