| A | B |
|---|
| ANTERIOR | (in animals and embryos) Pertaining to or toward the head or forward end of the body. (in humans) pertaining to or toward the front plane of the body, equivalent to the ventral surface of quadrupeds.,  |
| Bronchi | The two tubes that branch off from the lower end of the trachea, connecting it to the lungs, 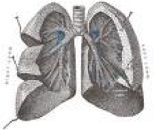 |
| Chromatin | The readily stainable substance of a cell nucleus, consisting of DNA, RNA, and various proteins, that forms chromosomes during cell division.,  |
| Deciduous | Plants and shrubs that shed foliage at the end of the growing season,  |
| Ecosystem | A system formed by the interaction of a community of organisms with their environment.,  |
| Fermentation | Is the process of deriving energy from the oxidation of organic compounds, such as carbohydrates, and using an endogenous electron acceptor, which is usually an organic compound, as opposed to Respiration where electrons are donated to an exogenous electron acceptor, such as oxygen.,  |
| Habitat | The natural environment of an organism; place that is natural for the life and growth of an organism a tropical habitat.,  |
| Involuntary Muscles | Muscles that we do not consciously control., 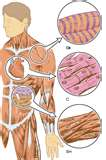 |
| Meiosis | A two-part cell division process in organisms that sexually reproduce, which results in gametes with one-half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell., 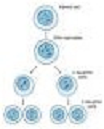 |
| Mutualism | A relationship between two species of organisms in which both benefit from the association.,  |
| Organ | Is a structure that contains at least two different types of tissue functioning together for a common purpose., 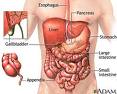 |
| Producer | (autotrophs) Utilize energy from the sun and nutrients from the abiotic environment (carbon dioxide from the air or water, other nutrients from the soil or water) to perform photosynthesis and grow., 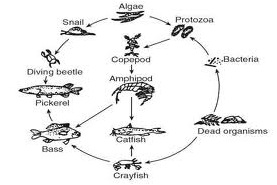 |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid any of a class of single-stranded molecules transcribed from DNA in the cell nucleus or in the mitochondrion or chloroplast, containing along the strand a linear sequence of nucleotide bases that is complementary to the DNA strand from which it is transcribed, 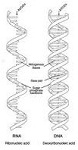 |
| Survival of the Fittest | A 19th century concept of human society. Inspired by the principle of natural selection, postulating that those who are eliminated in the struggle for existence are the unfit.,  |
| Vaccine | A preparation of a weakened or killed pathogen.,  |