| A | B |
|---|
| Adaptation | A characteristic that helps an organism survive its habitat.,  |
| Arteries | Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart., 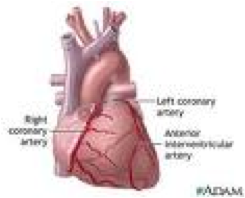 |
| Cell | A usually microscopic structure containing nuclear and cytoplasmic material enclosed by a semipermeable membrane and, in plants, a cell wall; the basic structural unit of all organisms., 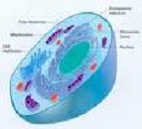 |
| Classification | Used to describe, and categorize all living things.,  |
| Disinfection | The destruction of all or most of the harmful microorganisms in an area by using chemicals called germicides,  |
| Endoderm | Is the innermost layer of the embryo.,  |
| Food Web | A series of organisms related by predator-prey and consumer-resource interactions, 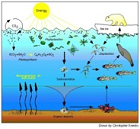 |
| Herbivore | An animal that feeds mainly or only on plants. In a food chain, herbivores are primary consumers.,  |
| Joint | A place where one bone is connected to another bone., 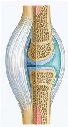 |
| Metaphase | Is a stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle in which condensed & highly coiled chromosomes, carrying genetic information, align in the middle of the cell before being separated into each of the two daughter cells. …, 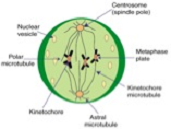 |
| Neurons | Cells that make up the nervous system, which receive and transmit information in the form of impulse., 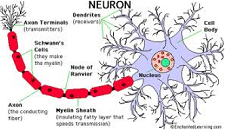 |
| Oviducts | Fallopian tube: either of a pair of tubes conducting the egg from the ovary to the uterus, 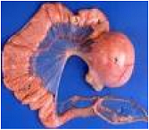 |
| Protein Synthesis | The creation of proteins by cells that uses DNA, RNA and various enzymes., 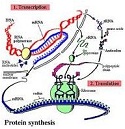 |
| Scavengers | An animal or other organism that feeds on dead organic matter,  |
| Tendon | A band of connective tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone., 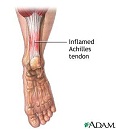 |
| Ventral | Toward or on or near the belly (front of a primate or lower surface of a lower animal); "the ventral aspect of the human body,  |