| A | B |
|---|
| Adaptive Radiation | The development of many different forms from an originally homogeneous group of organisms as they fill different ecological niches,  |
| Autotroph | Any organism capable of self-nourishment by using inorganic materials as a source of nutrients and using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis as a source of energy, as most plants and certain bacteria and protists.,  |
| Cell Membrane | The outer covering, or “skin,” of a cell which controls the flow of materials into and out of the cell., 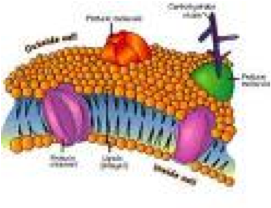 |
| Codon | A triplet of adjacent nucleotides in the messenger RNA chain that codes for a specific amino acid in the synthesis of a protein., 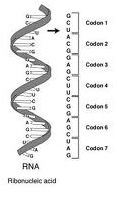 |
| Diversity | Diversity is variety, heterogeneity, multifarious, and difference,  |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | A network of tubular membranes within the cytoplasm of the cell, occurring either with a smooth surface (smooth endoplasmic reticulum) or studded with ribosomes’ (rough endoplasmic reticulum), involved in the transport of materials., 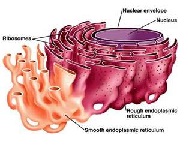 |
| Gametes | One of two haploid reproductive cells, male and female, whose union is necessary in sexual reproduction to initiate the development of a new individual.,  |
| Heterozygous | Of, or pertaining to an individual (or a condition in a cell or an organism) containing two different alleles for a particular trait,  |
| Kingdom | One of the three main divisions (animal, vegetable, and mineral) into which natural organisms and objects are classified.,  |
| Microtubules | One of the components of the cytoskeleton. They have a diameter of 25 nm and length varying from 200 nanometers to 25 micrometers. ..., 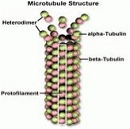 |
| Nitrogen Bases | Type of molecule that forms an important part of nucleic acid composed of a nitrogen-containing ring structure. Hydrogen bonds between bases in opposing complementary strands link the two strands of a DNA double helix., 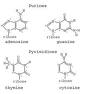 |
| Passive Transport | Means moving biochemical’s and other atomic or molecular substances across membranes., 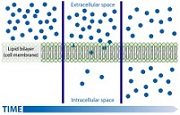 |
| Pupil | The hole through which light enters the eye., .jpeg) |
| Sexual Reproduction | Reproduction that involves two parents, producing offspring that are not identical with either parent., 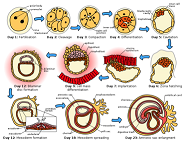 |
| Thymine | A pyrimidine base, C5H6N2O2, that is one of the principal components of DNA, in which it is paired with adenine,  |
| Virus | A small infectious agent that can replicate only inside the cells of other organisms,  |