| A | B |
|---|
| Alkali metal | An element in Group 1 of the periodic table.,  |
| Binary Compound | Compounded or consisting of two things or parts;characterized by two (things)., 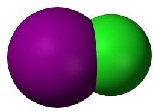 |
| Cloud Chamber | A sealed container of water vapor that has been supercooled and supersaturated. When a charged particle enters the chamber, it ionizes the vapor, causing it to condense within the chamber leaving a visible trail. Observation of the properties of these trails can provide information about the type of particle that caused them.,  |
| Decomposition Reaction | Separation of a substance into two or more substances that may differ from each other and from the original substance, 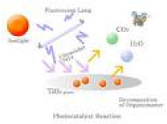 |
| Electromagnetic Induction | In physics, the induction of an electromotive force in a circuit by varying the magnetic flux linked with the circuit., 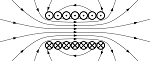 |
| Freezing Point | The temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a solid., 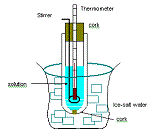 |
| Humus | The dark organic material in soils, produced by the decomposition of vegetable or animal matter and essential to the fertility of the earth,  |
| Ion | A charged atom or molecule. It is charged because the number of electrons does not equal the number of protons in the atom or molecule., 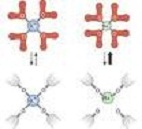 |
| Magnetic Pole | The end of a magnetic object, where the magnetic force is stronger., 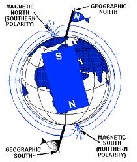 |
| Newton’s Law of Gravity | The principle that two particles attract each other with forces directly proportional to the product of their masses divided by the square of the distance between them, 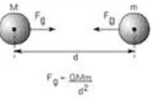 |
| Phase | Mechanically separate, homogeneous part of a heterogeneous system, 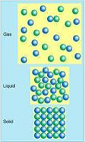 |
| Radiant Energy | The energy of electromagnetic waves. Radiant energy may be visible or invisible to the human eye.,  |
| Sodium Vapor | Light bulbs containing solid sodium plus neon and argon gas.,  |
| Suspension | A mixture in which particle,  |
| Vapors | Fumes or gases given off by a substance.,  |