| A | B |
|---|
| Alternating Current (AC) | Current consisting of charges that moves back and forth in a circuit., 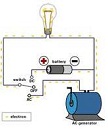 |
| Brushes | The contact points connected to a current source and the commutator of a motor., 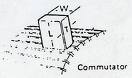 |
| Complex Carbohydrate | A substance consisting of long chains of simple carbohydrates.,  |
| Direct Current or DC | Electricity is the continuous movement of electrons from an area of negative (-) charges to an area of positive (+) charges through a conducting material such as a metal wire.,  |
| Electron | An elementary particle with negative charge,  |
| Fuel | A material that releases heat when it burns.,  |
| Hydrogen Ion | A positively charged ion (H+) formed of a hydrogen atom that has lost its electron., 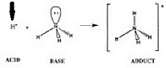 |
| Joule | A unit of electrical energy equal to the work done when a current of one ampere passes through a resistance of one ohm for one second,  |
| Mass Number | The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus., 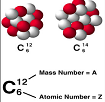 |
| Nomenclature | A system of names used in an art or science, 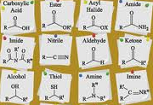 |
| Physical Change | A change from one state to another without a change in chemical composition,  |
| Radioactivity | The phenomenon, exhibited by and being a property of certain elements, of spontaneously emitting radiation resulting from changes in the nuclei of atoms of the element., 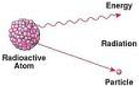 |
| Solute | The part of a solution present in a lesser amount and dissolved by the solvent.,  |
| Terminal Velocity | The maximum velocity of a falling object achieves., 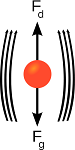 |
| Viscosity | The resistance of a liquid to flowing.,  |