| A | B |
|---|
| Amplitude | The maximum distance the particles of a medium move away from their rest positions as a wave passes through the medium.,  |
| Bubble Chamber | An instrument that records the tracks of ionizing particles,  |
| Compound | A substance made of two or more elements chemically combined.,  |
| Displacement | The displacing in space of one mass by another., 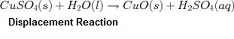 |
| Electron Cloud | An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus., 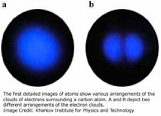 |
| Fulcrum | The fixed point around which a layer pivots., 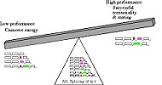 |
| Hydroxyl Group | The hydroxyl group is denoted by -OH in chemical structures and has a valence charge of -1., 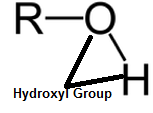 |
| Joule | The SI unit of work or energy, equal to the work done by a force of one newton when its point of application moves through a distance of one meter in the direction of the force., 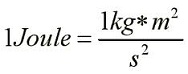 |
| Matter | A general term for the substance of which all physical objects are mad,  |
| Nonmetal | An element that lacks most of the properties of metals., .jpeg) |
| Physical Property | Any property used to characterize matter and energy and their interactions,  |
| Rarefaction | A rarefaction is a region in a longitudinal wave where the particles are furthest apart., 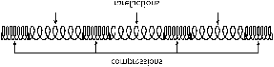 |
| Solution | A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances,  |
| The Law Of Conservation of Charge | States that the net charge of an isolated system remains constant.,  |
| Visible Light | Wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation that can be seen with the human eye.,  |