| A | B |
|---|
| Aqueous Solution | Is a solution in which the solvent is water., 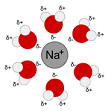 |
| Centripetal Force | A force that causes an object to move in a circle., 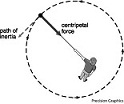 |
| Condensation | The changing of water vapor into droplets of liquid water; more generally, the change in phase from gas to liquid, 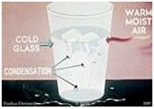 |
| Efficiency | The ratio of the output to the input of any system.,  |
| Energy Forms | Energy forms are either potential or kinetic. Potential energy comes in forms that are stored including — chemical, electrical, gravitational, mechanical, and nuclear. Kinetic energy forms are doing work — like heat, light, motion, and sound.,  |
| Glaciation | To become frozen or covered with ice or glaciers, 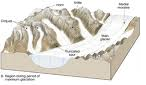 |
| Induction | The movement of electrons to one part of an object caused by the electric field of another object., 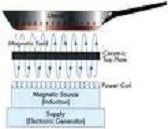 |
| Law of Conservation of Momentum | The principle that the total linear or angular momentum in any isolated system is constant, provided that no external force is applied., 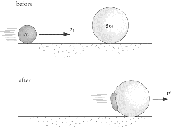 |
| Metal | An alloy or mixture composed wholly or partly of such substances, as brass.,  |
| Nuclear Reaction | Reaction involving the particles in the nucleus of an atom that can change an element into another element., 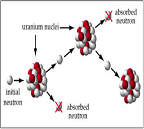 |
| Polarized Light | Light that vibrates in only one direction.,  |
| Replacement Reaction | Reaction in which one element replaces another in a compound, or in which two elements in different compounds trade places., 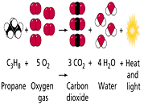 |
| Standing Wave | A wave that appears to stand in one place, even though it is two waves interfering as they pass through each other, 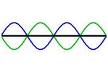 |
| Transceiver | A device that has both a transmitter and a receiver which are combined and share common circuitry or a single housing.,  |
| Wavelength | The distance between the crest of one wave and the crest of the next., 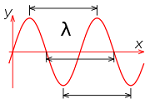 |