| A | B |
|---|
| Atom | The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense, central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons., 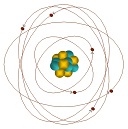 |
| Ceramic | A hard, crystalline solid made by heating clay and other mineral materials to high temperatures,  |
| Condensation Point | The temperature at which a material changes from a gas to a liquid; the same as the boiling point.,  |
| Elastic Potential Energy | Is the energy that is stored by the forces within a distorted elastic object., 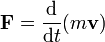 |
| Entropy | A numerical measure of the uncertainty of an outcome., 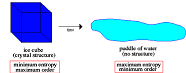 |
| Glass | A clear, solid material with no crystal structure, created by heating sand to a very high temperature,  |
| Inertia | The tendency of a body to maintain its state of rest or uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force,  |
| Law of Reflection | When a ray of light strikes a plane mirror, the light ray reflects off the mirror. Reflection involves a change in direction of the light ray. The convention used to express the direction of a light ray is to indicate the angle which the light ray makes with a normal line drawn to the surface of the mirror. The angle of incidence is the angle between this normal line and the incident ray; the angle of reflection is the angle between this normal line and the reflected ray. According to the law of reflection, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection., 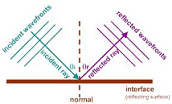 |
| Metal | A chemical element that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat and forms cations and ionic bonds with non-metals.,  |
| Nucleus | The central core of an atom containing protons and usually neutrons,  |
| Polyatomic Ion | An ion that is made of more than one atom.,  |
| Resistance | The opposition to the movement of electric charges flowing through a material, 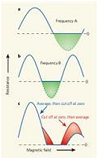 |
| Starch | A complex carbohydrate in which plants store energy, 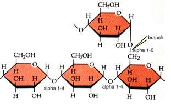 |
| Transeverse Wave | A transverse wave is a moving wave that consists of oscillations occurring perpendicular (or right angled) to the direction of energy transfer., 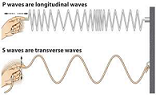 |
| Weak Acid | Is an acid that does not fully ionize in solution; that is, if the acid was represented by the general formula AH, then in aqueous solution a significant amount of undissolved AH still remains.,  |