| A | B |
|---|
| Alcohol | A substitute hydrocarbon that contains one or more hydroxyl groups.,  |
| Binary Compound | A binary compound is a chemical compound that contains exactly two different elements. Examples are NaCl (sodium chloride), NaF (sodium fluoride), and MgO (magnesium oxide). Can be either molecular or ionic.,  |
| Circuit Breaker | A safety device that uses an electromagnet to shut off a circuit when the current is too high., 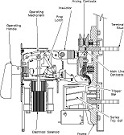 |
| Decibel | Is the unit used to measure the intensity of a sound.,  |
| Electromagnetic Energy | The energy of light and other forms of radiation.,  |
| Freezing | The change in phase from liquid to solid.,  |
| Homogeneous Mixture | A homogeneous mixture has the same uniform appearance and composition throughout.,  |
| Interval | A space between two objects, points, or units.,  |
| Magnetic Field Lines | Lines that map out the magnetic field around a magnet., 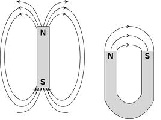 |
| Newton’s Third Law of Motion | For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.,  |
| pH Scale | Ranged of values from 0 to 14 that expresses the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution.,  |
| Quark | Are the building blocks which build up matter. Located inside the nucleus.,  |
| Slip Rings | Connection consisting of a metal ring on a rotating part of a machine; provides a continuous electrical connection through brushes on stationary contacts, 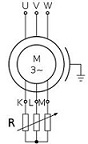 |
| Surface Wave | A wave that occurs at the surface between two mediums,  |
| Vaporization | The change from the liquid to the gaseous state of matter, 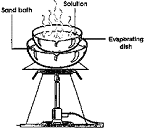 |