| A | B |
|---|
| Ribosomes | Are the components of cells that make proteins from all amino acids., 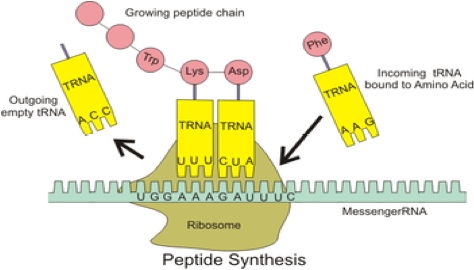 |
| Anticodon | Is a small RNA molecule (usually about 73-95 nucleotides) that transfers a specific active amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain at the ribosomal site of protein synthesis during translation., 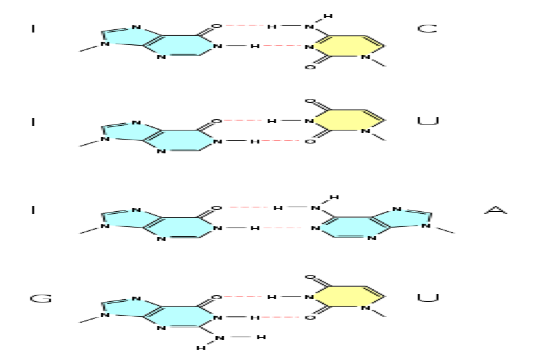 |
| Double Helix | A pair of parallel helices intertwined about a common axis,  |
| DNA | A long linear polymer found in the nucleus of a cell and formed from nucleotides and shaped like a double helix; associated with the transmission of genetic information,  |
| Thymine | A base found in DNA (but not in RNA) and derived from pyrimidine; pairs with adenine, 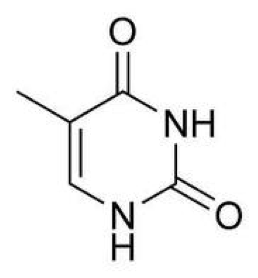 |
| Cytosine | One of the four types of 'base' that spells out our DNA code, 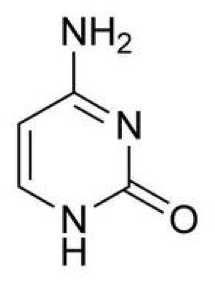 |
| Guanine | A nucleic base and pairs with cytosine in DNA and RNA, 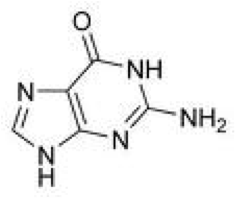 |
| Uracil | One of the five main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, 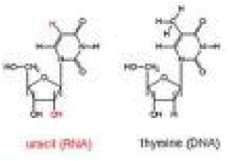 |
| Hydrogen Bond | The attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom.,  |
| Replication | The process by which double-stranded dna makes copies of itself, 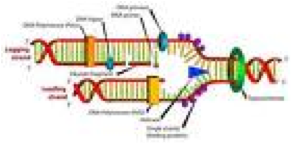 |
| Transcription | The organic process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA; the process whereby a base sequence of messenger RNA is synthesized on a template of complementary DNA, 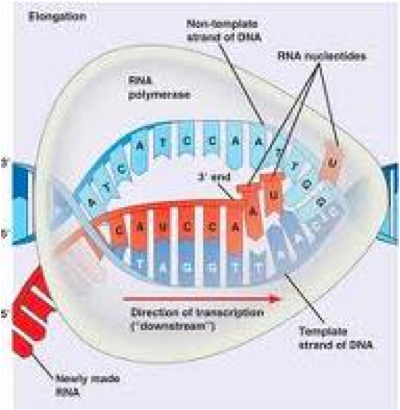 |
| Translation | The process whereby genetic information coded in messenger RNA directs the formation of a specific protein at a ribosome in the cytoplasm, 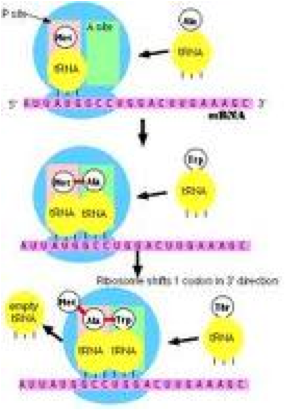 |
| Nucleus | A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction,  |
| RNA (ribonucleic acid) | A long linear polymer of nucleotides found in the nucleus but mainly in the cytoplasm of a cell where it is associated with microsomes; it transmits genetic information from DNA to the cytoplasm and controls certain chemical processes in the cell, 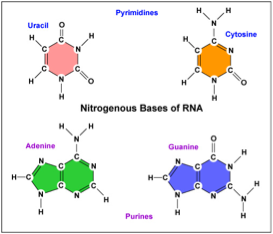 |
| Nitrogen Base | The basic component of nucleic acids; composed of a nitrogen-containing molecule of purine or pyrimidine., 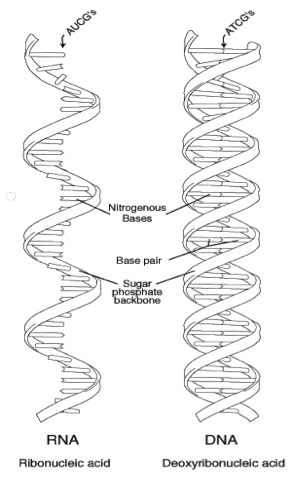 |
| Adenine | Purine base found in DNA and RNA; pairs with thymine in DNA and with uracil in RNA, 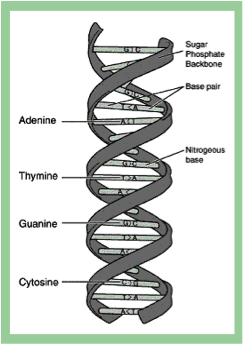 |
| Codon | A sequence of three nucleotides which code for an amino acid, 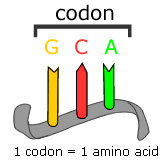 |