| A | B |
|---|
| Atmosphere | The mixture of gases surrounding the Earth or other celestial body, held in place by gravity.,  |
| Axial Tilt | The way the earth tilts, 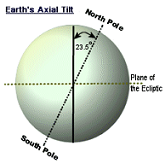 |
| Climate | The general or average weather conditions of a certain region, including temperature, rainfall, and wind.,  |
| Conduction | The transfer of heat between two parts of a stationary system, caused by a temperature difference between the parts., 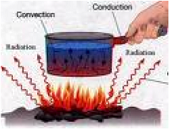 |
| Convection | The transfer of heat through a fluid (liquid or gas) caused by molecular motion., 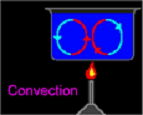 |
| Day | Traditionally defined as the span of time it takes for the Earth or a celestial body (such as an other planet or a moon) to make a single rotation with respect to a star, measured most accurately from local noon to local noon.,  |
| Earth | The 3rd planet from the sun; the planet we live on; "the Earth moves around the sun".,  |
| Eclipse | When the moon goes in front of the sun.,  |
| Energy | The capacity for vigorous activity; available power, 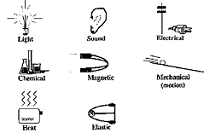 |
| Greenhouse Effect | Warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere; caused by atmospheric gases that allow sunshine to pass through but absorb heat that is radiated back from the warmed surface of the earth, 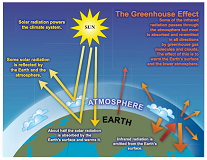 |
| Greenhouse Gases | Vapors, including water, in the lower atmosphere, which reflect solar radiation back to earth.,  |
| Heat Energy | A type of energy associated with temperature. Actual amounts of heat energy are difficult to measure., 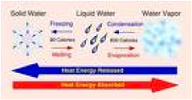 |
| Heat Source | A medium or container from which heat flows., 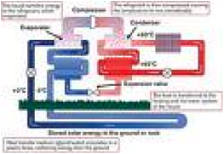 |
| Heliocentric | Is the astronomical theory that the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun and that the Sun is stationary and at the center of the universe., 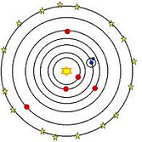 |
| Ocean Current | An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon it's flow., 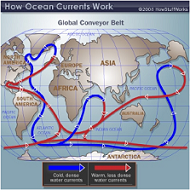 |
| Radiation | Energy that is radiated or transmitted in the form of rays or waves or particles., 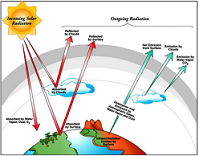 |
| Revolution | Describes the movement of the earth around the sun over a period of one year, causing seasons to occur., 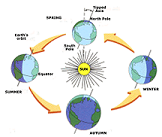 |
| Rotation | A rotation is a movement of an object in a circular motion., 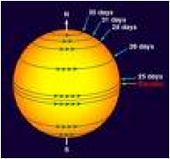 |
| Season | One of four natural divisions of the year—spring, summer, autumn, and winter—in temperate zones.,  |
| Solstice | Either of the two times of the year when the sun is at its greatest distance from the celestial equator., 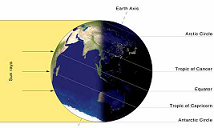 |
| Sun | A self-luminous heavenly body; star., 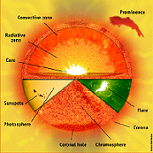 |
| Weather | How hot or cold, wet or dry, stormy or calm it is in an area over a short period of time.,  |
| Wind | The flow of gases on a large scale.,  |
| Year | A period of time occupying a regular part of a calendar year that is used for some particular activity; "a school year"., 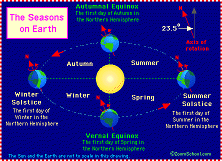 |