| A | B |
|---|
| Atom | Is a basic unit that makes up all matter.,  |
| Bond | The chemical force that holds atoms together in a molecule.,  |
| Ionic Bond | Between two ions with opposite charges, characteristic of salts.,  |
| Covalent Bond | A form of chemical bonding that is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms., 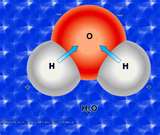 |
| Compound | To combine so as to form a whole; mix.,  |
| Electron | An electron is a negatively charged subatomic particle., 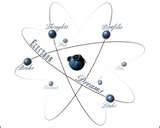 |
| Nucleus | A central part about which other parts are grouped or gathered; core, 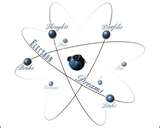 |
| Proton | Elementary particle having a single positive electrical charge and constituting the nucleus of the ordinary hydrogen atom., 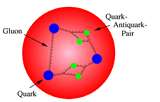 |
| Neutron | A subatomic particle with no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton., 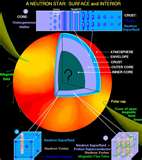 |
| Atomic Number | The number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus., 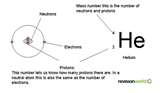 |
| Mass Number | The total number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus.,  |
| Isotope | Atoms that contain the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons., 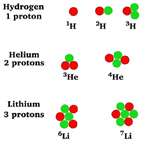 |
| Ion | Atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge.,  |
| Nuclear Reactions | The process in which two nuclei or nuclear particles collide to produce products different from the initial particles.,  |
| Radioactivity | Particles which are emitted from nuclei as a result of nuclear instability.,  |
| Radiation | Process in which energetic particles or waves travel through a medium or space.,  |
| Carbon Dating | A variety of radioactive dating which is applicable only to matter which was once living and presumed to be in equilibrium with the atmosphere, taking in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis.,  |
| Alpha | Particles or particles consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus.,  |
| Beta | Decay (sometimes called neutron decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (an electron or a positron) is emitted.,  |
| Gamma | Form of ionizing radiation; they are more penetrating than either alpha or beta radiation (neither of which is electromagnetic radiation), but less ionizing.,  |