| A | B |
|---|
| Nebula | A diffuse mass of interstellar dust or gas or both, visible as luminous patches.,  |
| Main Sequence | A continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness., 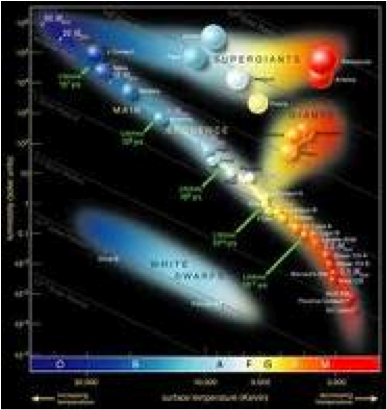 |
| Supergiant | An extremely bright star of very large diameter and low density.,  |
| Hertzsprung Russell | A graph of stars. It plots each star on the graph in accordance with it's absolute magnitude or it's brightness against it's color and temperature., 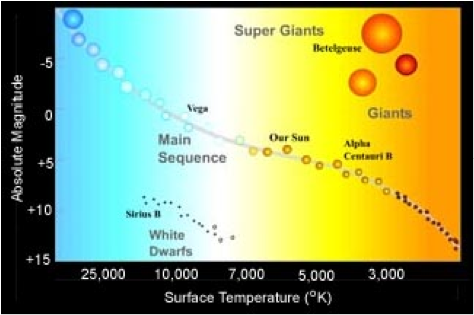 |
| Temperature | A measure of the warmth or coldness of an object or substance with reference to some standard value.,  |
| Star Formation | Is the process by which dense parts of molecular clouds collapse into a ball of plasma to form a star.,  |
| Universe | All matter and energy, including the earth, the galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space, regarded as a whole.,  |
| Galaxy | Any of numerous large-scale aggregates of stars, gas, and dust that constitute the universe, containing an average of 100 billion (1011) solar masses and ranging in diameter from 1,500 to 300,000 light-years.,  |
| Star | A self-luminous celestial body consisting of a mass of gas held together by its own gravity in which the energy generated by nuclear reactions in the interior is balanced by the outflow of energy to the surface, and the inward-directed gravitational forces are balanced by the outward-directed gas and radiation pressures.,  |
| Kelvin | A unit of absolute temperature equal to 1/273.16 of the absolute temperature of the triple point of water. One kelvin degree is equal to one Celsius degree.,  |
| Absolute Magnitude | The intrinsic magnitude of a celestial body computed as if viewed from a distance of 10 parsecs, or 32.6 light-years,  |
| Apparent Magnitude | Astronomy The degree of brightness of a celestial body designated on a numerical scale, on which the brightest star has magnitude -1.4 and the faintest visible star has magnitude 6, with the scale rule such that a decrease of one unit represents an increase in apparent brightness by a factor of 2.512. Also called apparent magnitude.,  |