| A | B |
|---|
| Base | Any of various water-soluble compounds capable of turning litmus blue and reacting with an acid to form a salt and water; "bases include oxides and hydroxides of metals and ammonia",  |
| Reaction Rate | An equation describing the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs in units of mol vol^-1 time^-1., 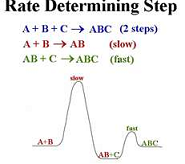 |
| Catalyst | A substance that initiates or accelerates a chemical reaction without itself being affected,  |
| Physical Property | A physical property is any measurable property the value of which describes a physical system's state at any given moment in time. For that reason the changes in the physical properties of a system can be used to describe its transformations (or evolutions between its momentary states).,  |
| Chemical Property | A chemical property is any of a material's properties that becomes evident during a chemical reaction; that is, any quality that can be established only by changing a substance's chemical identity,  |
| Conservation of Energy | The total amount of energy in an isolated system remains constant over time,  |
| Conservation of Matter | The mass of an isolated system cannot be changed as a result of processes acting inside the system.,  |
| Chemical Reaction | A process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another.,  |
| Chemical Energy | The form of energy that is used most often.,  |
| Exothermic Reaction | Is a chemical reaction that releases energy in the form of heat. It is the opposite of an endothermic reaction.,  |
| Endothermic Reaction | Is any chemical reaction that absorbs heat from its environment.,  |
| Reactant | A substance participating in a chemical reaction, especially one present at the start of the reaction.,  |
| Product | A substance formed in a chemical reaction.,  |
| Acid | A chemical species that donates protons or hydrogen ions and/or accepts electrons., 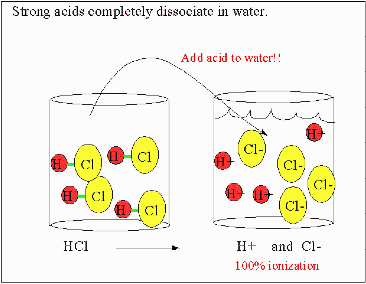 |