| A | B |
|---|
| Abiotic | Not associated to life,  |
| Autotroph | An organism that produces complex organic compounds (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) from simple inorganic molecules using energy from light (by photosynthesis) or inorganic chemical reactions. They are able to make their own food and can fix carbon dioxide.,  |
| Biodiversity | The variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or for the entire Earth.,  |
| Biome | A major biotic community characterized by the dominant forms of plant life and the prevailing climate,  |
| Biotic | Pertaining to life, 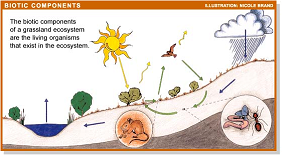 |
| Carnivores | Organism that eats meat,  |
| Consumer | An organism that uses energy for fuel,  |
| Decomposers | Any organism that feeds off decomposing organic material, such as dead leaves, dropped fruits, wood and dead animals, 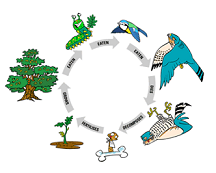 |
| Ecology | The branch of biology dealing with the relations and interactions between organisms and their environment, including other organisms.,  |
| Ecosystem | A system formed by the interaction of a community of organisms with their physical environment,  |
| Energy Transfer | The transfer of energy from one body to another, 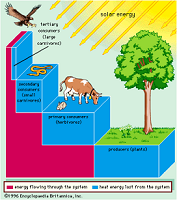 |
| Food Chain | Representations of the predator-prey relationships between species within an ecosystem or habitat., 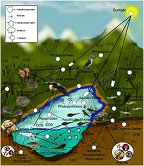 |
| Food Web | Graphical description of feeding relationships among species in an ecological community, that is, of who eats whom, 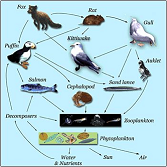 |
| Herbivores | Organism that eats plants,  |
| Heterotroph | An organism that uses organic carbon for growth, 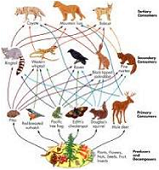 |
| Homeostasis | Ability of a system or living organism to adjust its internal environment to maintain a stable equilibrium; such as the ability of warm-blooded animals to maintain a constant temperature; Such a dynamic equilibrium or balance, 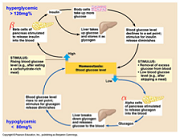 |
| Niche | A term describing the relational position of a species or population in its ecosystem to each other,  |
| Producers | utilize energy from the sun and nutrients from the abiotic environment (carbon dioxide from the air or water, other nutrients from the soil or water) to perform photosynthesis and grow.,  |
| Scavengers | A carnivorous feeding behavior in which a predator consumes corpses or carrion that were not killed to be eaten by the predator or others of its species,  |
| Trophic Level | The position it occupies on the food web.,  |