| A | B |
|---|
| Amino Acid | Molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side chain that varies between different amino acids., 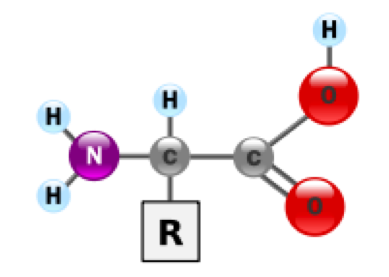 |
| Carbohydrates | Any of a class of organic compounds that are polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones, or change to such substances on simple chemical transformations, as hydrolysis, oxidation, or reduction, and that form the supporting tissues of plants and are important food for animals and people.,  |
| Cell Structures | An organelle, or the layout of organelles of the biological cell itself., 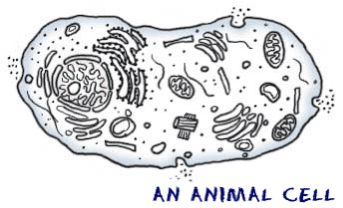 |
| Cell wall | The tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells.,  |
| Chloroplasts | Organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis, 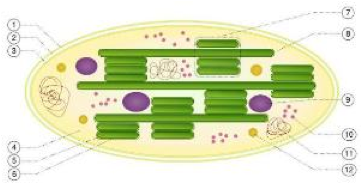 |
| Cytoplasm | A thick liquid residing between the cell membrane holding organelles, except for the nucleus., 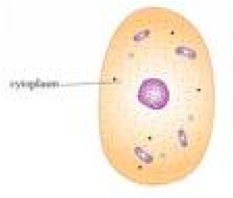 |
| Diffusion | Describes the spread of particles through random motion from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration., 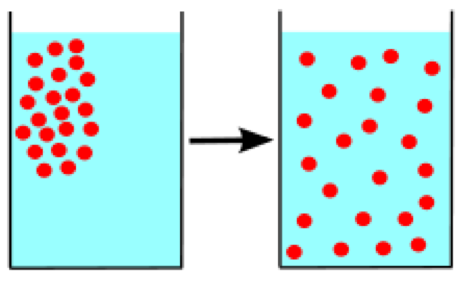 |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Eukaryotic organelle that forms an interconnected network of tubules, vesicles, and cisternae within cells, 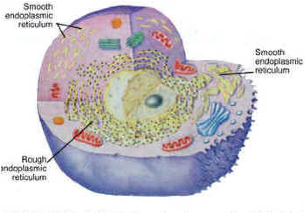 |
| Golgi Body | Stacked, flattened membranes which sort proteins and other cellular substances and package them into membrane-bound structures called vesicles., 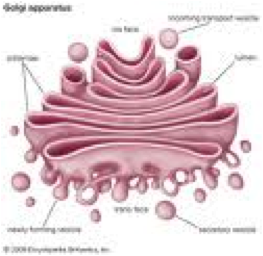 |
| Hemoglobin | The iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all vertebrates and the tissues of some invertebrates., 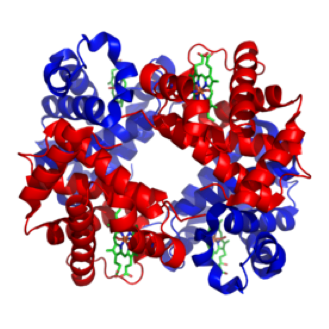 |
| Lipids | Any of a group of organic compounds that are greasy to the touch, insoluble in water, and soluble in alcohol and ether, 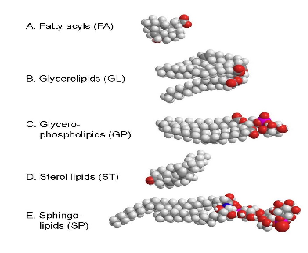 |
| Membrane | An enclosing or separating membrane that acts as a selective barrier, within or around a cell., 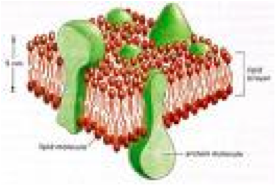 |
| Metabolism | Set of chemical reactions that happen in living organisms to maintain life., 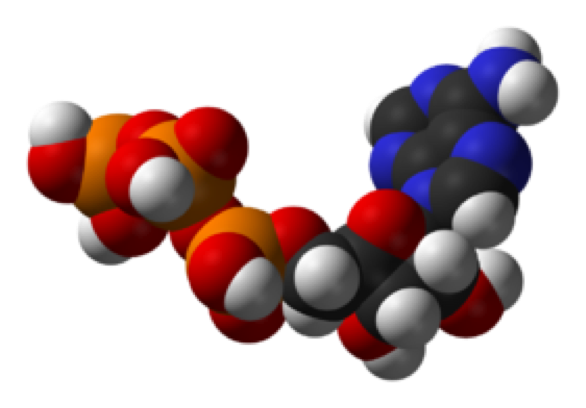 |
| Mitochondria | In cell biology, a mitochondrion (plural mitochondria) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. These organelles range from 0.5 to 10 micrometers (?m) in diameter. ...,  |
| Nucleus | A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction, 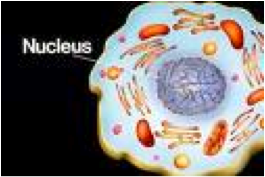 |
| Organ | A part of the body that performs a specific function. For example, the heart is an organ., 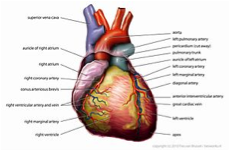 |
| Organ Systems | Is the cardiovascular system, which includes the heart (cardio) and blood vessels (vascular)., 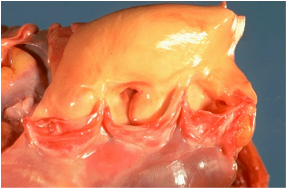 |
| Osmosis | The movement of water molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane down a water potential gradient.,  |
| Polypeptide | A chain of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds and having a molecular weight of up to about 10,000.,  |
| Protein | Any of numerous, highly varied organic molecules constituting a large portion of the mass of every life form and necessary in the diet of all animals and other nonphotosynthesizing organisms, composed of 20 or more amino acids linked in a genetically controlled linear sequence into one or more long polypeptide chains, the final shape and other properties of each protein being determined by the side chains of the amino acids and their chemical attachments., 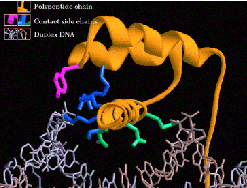 |
| Ribosomes | Ribosomes are the components of cells that make proteins from amino acids. One of the central tenets of biology is that DNA makes RNA, which then makes protein. The DNA sequence in genes is copied into a messenger RNA (mRNA)., 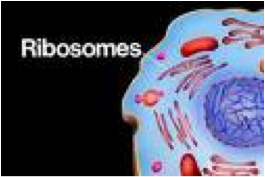 |
| Tissue | Is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism.,  |