| A | B |
|---|
| Form of cell dividion that halves the number of chromosomes | Meiosis |
| The purpose of Meiosis | To produce gametes (egg and sperm) |
| Occurs when portions of homologous chromosomes are exchanged | Crossing-0ver, 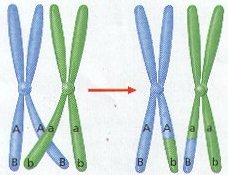 |
| Meiosis in males is called spermatogenesis and results in the production of | 4 sperm cells |
| Meiosis in females is called oogenesis and results in the production of | 4 eggs cells (only one survives) |
| A haploid sperm cell unites with a haploid egg cell to produce a diploid zygote during | Fertilization |
| Type of reproduction in which one parent passes all of its chromosomes to its offspring | Asexual Reproduction |
| Type of reproduction in which two parents each provide half of the chromosomes to the offspring | Sexual Reproduction |
| An organism identical to its parent - asexual reproduction | Clone |
| Number of "parent" cells at the start of Meiosis | One |
| Number of chromosomes in "parent" cell at the start of Meiosis | Diploid (2n) |
| Number of "daughter" cells at the end of Meiosis | Four |
| Number of chromosomes in "daughter" cells at the end of Meiosis | Haploid (n) |