| A | B |
|---|
Input Devices,  | sends info from the user to CPU (mouse, keyboard, microphones) |
CPU,  | central processing unit; Brains of the computer |
Output Devices, 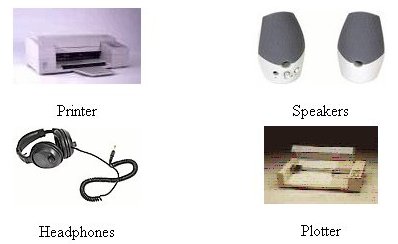 | sends info from the CPU to user (printer, monitor, speakers) |
| Binary Code | the basics of all computers; 1 = on/true; 0 = off/false |
Supercomputers are:,  | series of big computers "chained together" to work as 1 |
Charles Babbage,  | "father" of computers; had the idea for computers in the 1830's |
The Analytical Machine, 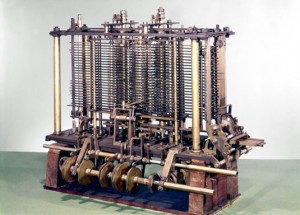 | design for computer by Charles Babbage but never built due to lack of money and design issues |
Herman Hollerith,  | MIT Professor who created the Hollerith Census Tabulator |
Hollerith Census Tabulator,  | made for 1890 census to speed up process of counting census cards; done in 6 weeks vs 10 years; punch card computer system |
Colossus Computer, 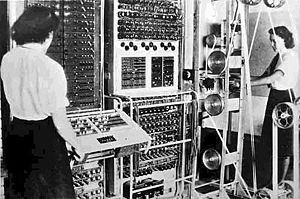 | first electronic digital computer made in World War II to break German Enigma machine codes |
ENIAC,  | built in 1943-45; electronic general purpose computer to solve many different problems |
| Univac stands for: | Universal Automatic Computer |
Univac was:,  | first mainframe computer commercially sold and mass produced; size of a typical classroom |
NASA needed Computer Guidance System,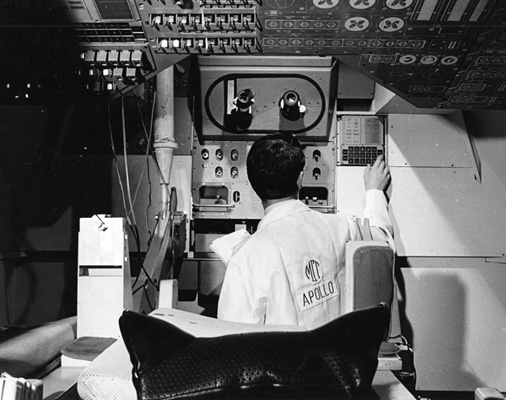  | since pencils/paper & slide rules couldn't be used in space |
NASA's computer needed,  | to be smaller than mainframe to fit on space craft and included integrated circuits |
Integrated circuits,  | invented in 1959, consisted of a network of silcon on a single chip |
Transistors,  | invented by Bell Labs and replaced vacuum tubes, made of silicon and tiny wires |
| 3 things that made smaller computers possible | transitors, integrated circuits and microprocessors |
| microprocessor | developed by Intel; was an integrated circuit including a processor (tiny computer) |
Alto Computer made,  | by Xerox in 1973 |
ALTO Computer,  | first microcomputer with GUI, mouse, built-in networking and laser printer for $18,000 |
GUI, 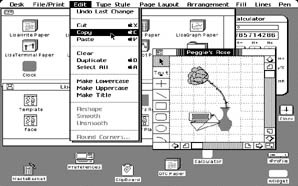 | Graphic User Interface; ability to use mouse to click on items and get a menu |
| Altair | first microcomputer; non-programmed, no monitor, no keyboard, no GUI |
PC,  | personal computer; name of IBM's first home computer; also the general name of all Intel based computers (non-Mac's) |
Windows Operating System, 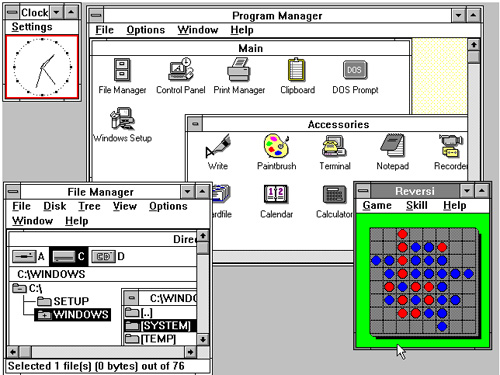 | Microsoft's first GUI-mouse based OS; inspired by Apple's operating system |
| WWW | world wide web; aka The Internet; widely available in the mid-1990's |
| Herman Hollerith Legacy | Herman Hollerith's company eventually would become IBM, one of the biggest computer companies in the world |
Yahoo,  | founded by Jerry Yang & David Filo at Stanford University in 1994,  |
| How Yahoo worked | it is a web directory |
| search engine | A program for the retrieval of data, files, or documents from the Internet. |
| Examples of search engines | Yahoo, Google, Excite, Lycos, Dogpile....,  |
| Yahoo started: | as a way to collect websites to win a fantasy basketball league |
| how Yahoo makes money | used banner ads on Yahoo pages to generate revenue/income |
| web directory | Human manual catalogging of websites by subject, often providing brief descriptions of each website’s content |
Excite,  | started in 1994 at Stanford University |
| How Excite worked | used web crawlers to find search results automatically without human interaction |
| How Excite made money | used banner ads on Excite pages to generate revenue/income |
| web crawlers | a computer program that browses the World Wide Web in a methodical, automated manner and reports back back to a search engine with results |
Google,  | founded by Sergey Brin and Larry Page at Stanford University in 1998,  |
| How Google Works | uses a web crawler to find websites and count the number of in-links for search results with higher results listed higher on the search list |
| "In-Links" | when a website is listed by other websites |
| Google's name | named GOOGLE after the mathematical term googol which means 1 followed by 100 zeros or 1 to the 100th power, 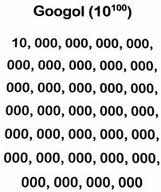 |
| Google's company motto | “Don’t be evil”,  |
| the verb "to Google" | means searching for something on the Internet |
| How Google made money | purposely did not use banner ads to generate income but “pirated” the idea of sponsored links to generate income |
| Adwords | using keywords typed in a search to generate related sponsored ad’s in a search query,  |
| ARPANET | Advanced Research Projects Agency Network, 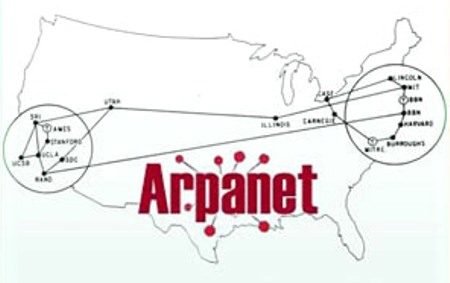 |
| What is ARPANET | allowed offices and campuses across the country to connect together to work together on projects for the Department of Defense |
| When ARPANET started | 1959 |
| dot-com bubble | the founding of a group of new Internet-based companies commonly referred to as dot-coms from 1995-2000 |
| Web Bubble Burst | 2000-2001 when over 50% of newer Tech companies closed up or greatly scaled back production and many investors lost billions of dollars at this time |
| Stanford University | major Ivy League university in California, outside of San Francisco where Yahoo, Excite and Google were founded,  |
| web browser | program installed to your computer that allows you to access the internet |
| web browser examples | Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari, and Internet Explorer,  |
| BING | Microsoft's search engine,  |
| what does BING stand for | Because It's Not Google |
| Alphabet | the parent company of Google run by Larry Page & Sergey Brin |
| Deep Web definition | web pages that can't be found with search engines because they are encrypted or private pages |
| examples of Deep Web | private Google account documents or any site that requires a password to access |
| Dark Web definition | Sites that are purposely kept private for specific reasons, sometimes illegal reasons or for privacy concerns |
Microsoft,  | software company that created Windows OS, Office (Word, Excel, Power Point) and MS-DOS |
| Founders of Microsoft | Bill Gates & Paul Allen,  |
Bill Gates,  | founder of Microsoft with "gambling" personality, impulsive but smart, possibly ADHD |
Steve Ballmer,  | previous CEO of Microsoft; college friend of Bill Gates |
| Harvard University | school attended by Bill Gates (he didn't graduate) and Steve Ballmer (he did graduate) |
| Microsoft's first tech innovation | wrote BASIC programming language for MITS/Altair computer |
MITS/Altair,  | first microcomputer (aka Personal Computer aka PC) |
| How Microsoft makes their money | by licensing software to individual computers (not selling the copyright of software to a company) |
MS-DOS,  | software owned by Microsoft that they bought from Seattle Computer Company |
| GUI | Graphic User Interface |
Reunion of Microsoft & Apple,  | in 1997 Microsoft invested $150 million dollars into apple, becoming a major stockholder |
Apple,  | computer company create by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak |
Steve Jobs,  | founder of Apple, experimental personality (drugs, religions, therapies...), charming but didn't treat people nicely |
| Evil Genius | nickname of Steve Jobs,  |
Steve "Woz" Wozniak,  | co-founder of Apple Computers; was the original inventor of computers for Apple |
| Apple's first tech innovation | used "Blue Box" to steal long distance telephone service from AT&T; idea came from hacker called Captain Crunch |
IBM,  | makers of main frame computers (in 70's and 80's) who Steve Jobs compared to Big Brother |
HP,  | turned down opportunity to create Woz's first computer The Apple I in 1976 |
Apple II,  | personal computer with CPU, keyboard, color graphics and floppy disk; launched personal computer industry |
The Lisa,  | First computer using GUI and mouse sold to the public |
Xerox,  | originally created the idea of GUI and the mouse; both Apple and Microsoft "pirated" the idea of Xerox |
The Macintosh,  | Rival of The Lisa, and the subject of the infamous 1984 Apple Super Bowl Commercial |
| Steve Jobs Fired from Apple | in 1985 due to conflicts with CEO Jack Sculley and the Board of Directors |
Pixar Animation Studios,  | a company that Steve Jobs bought that was later bought by Disney |
| Reunion at Apple | Steve Jobs rehired as CEO of Apple in 1997; revitalized Apple with products such as iPod, MacAir, MacBook, iTunes, iPhone and iPad |
Apple I,  | first computer that Woz and Steve Jobs made as Apple Computers; made of wood |
| operating system | the "master" software program on a computer that allows all other functions and software to work |
| Examples of Operating Systems | Apple OS, Windows 7, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Linux, Unix, MS-DOS, Android... |