| A | B |
|---|
| Keratitis | Inflammation or infection of the cornea |
Chalazion, 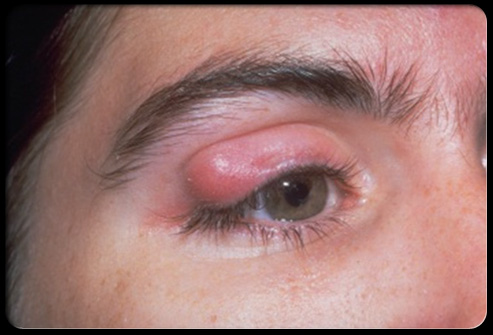 | Chronic inflammatory granuloma of the meibomian (sebaceous glands in the lid |
Conjunctivitis,  | Infection or inflammation of the conjunctiva |
| Keratoconjunctivitis | Dry eyes |
Strabismus, 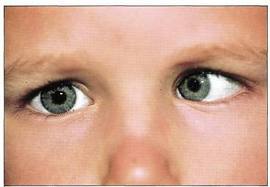 | Inability to focus on two things at one time |
Cataract, 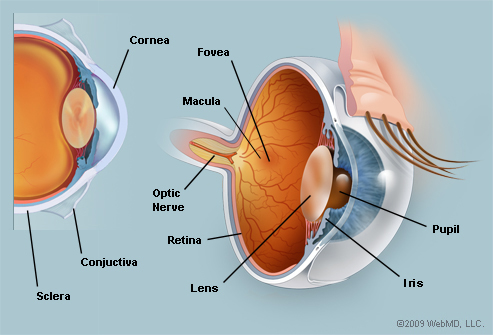 | Opacity within the lens |
Retinopathy, 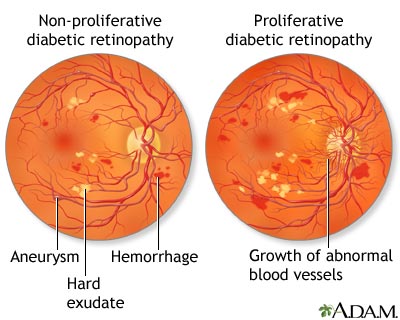 | Microvascular damage to the retina causing blurred vision and progressive vision loss |
Glaucoma, 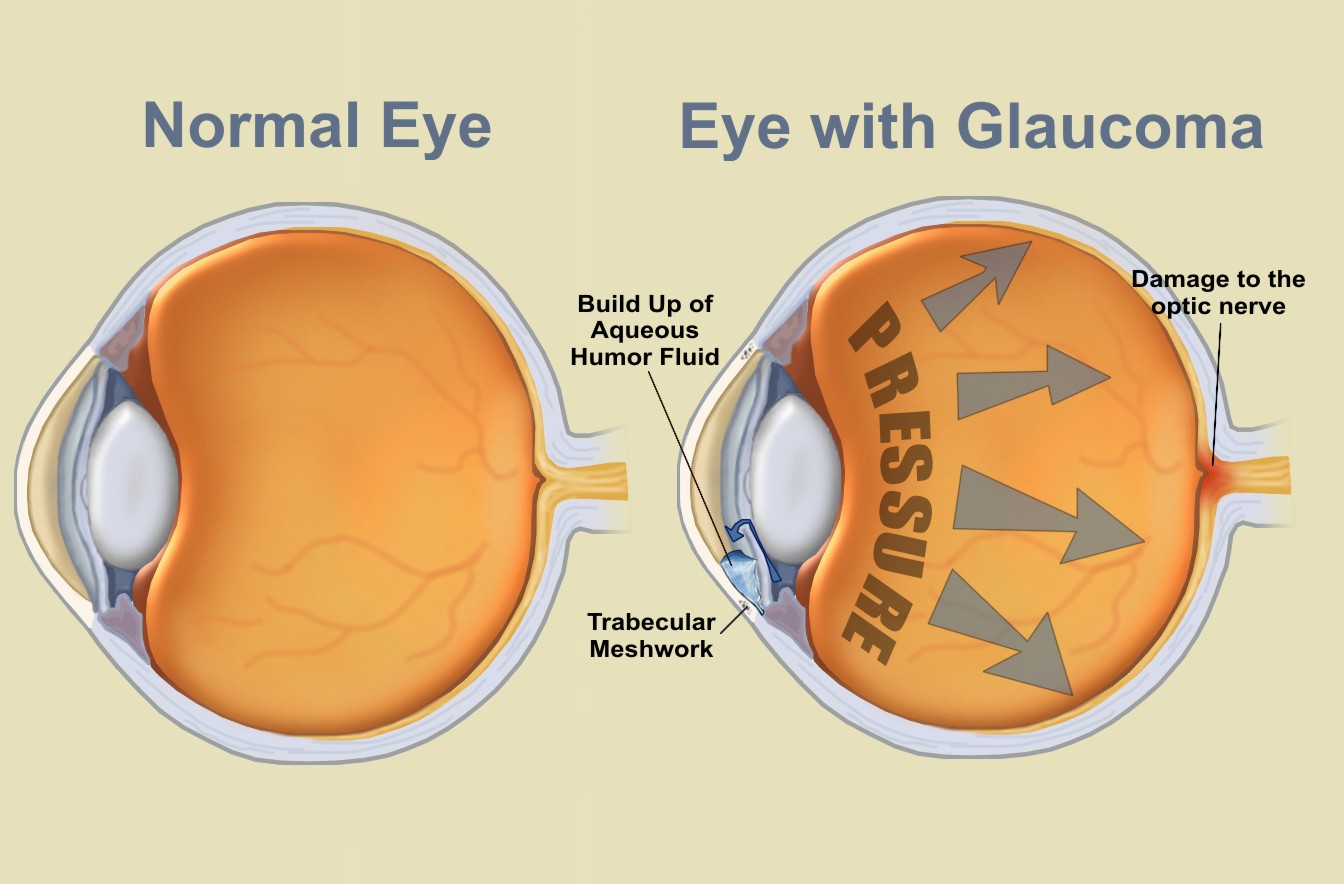 | Increased intraoccular pressure, optic nerve atrophy, and periperal vision loss. Diagnosed by: History adn physical exam, visual acuity measurement, tomometry, ophthalmoscopy (direct and indirect), slit lamp microscopy, gonioscopy, visual field perimetry, fundus photography. |
Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma, 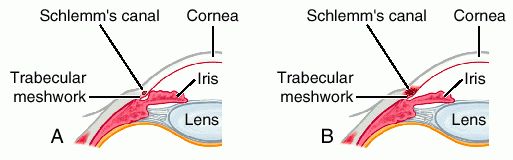 | Emergency requiring immediate lowering of intraoccular pressure |
Enuculeation,  | Removal of the eye |
Hordeolum, .jpg) | An infection of the sebaceous gland of the eye lid |
| Meniere's Disease | results in accumulation of endolymph in the labyrinth. Symptoms include: episodic vetigo, tinnitus, fluctuating hearing loss, and aural fullness. |
Otosclerosis, 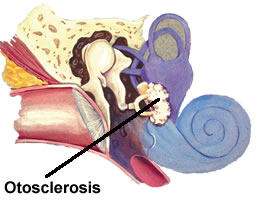 | autosomal dominant disease, is the fixation of the footplate of the stapes in the oval window and, a cause of conductive hearing loss |
| Acoustic neuroma | benign tumor that occurs when the acoustic nerve (CN VIII) enters the internal auditory canal or temporal bone from the brain |
| Labyrinthitis | inflammation of the inner ear affecting the cochlear and/or vestibular portion of the labyrinth |
| Betaxolol (Betoptic) | Beta1 cardioselective blocker; decreases aqueous humor production. Side Effects: transient discomfort; systemic reactions rarely reported but include bradycardia, heart block, pulmonary distress, headache, depression. |
| cholesteatoma | a mass of epithelial cells and cholesterol in the middle ear. |
| Teaching After Ear Surgery | 1. Avoid sudden head movements 2. Do not try to get out of bed without assistance. 3. Take antivertigo agents as prescribed. 4. Change positions slowly. 5. Avoid getting the head wet including showering until directed by surgeon. 6. Report fever, pain, increase in hearing loss, or drainage from the ear. 7. Do not cough or blow the nose because this causes increased pressure in the eustacian tube and middle ear cavity and disrupts healing. 8. If need to cough or sneeze, leave the mouth open to help reduce the pressure. 9. Avoid crowds where respiratory infections may be contracted. 10. Avoid situations where pressure or popping in the ears is normally experienced, such as high elevations or airplane travel. |
| Refraction | the ability of the eye to bend light rays so that they fall on the retina. |
| Emmetropia | Light is focused exactly on the retina, not in front of it or behind it. |
Myopia,  | Ability to see near objects clearly (near-sightedness), but objects in the distance are blurred. |
Hyperopia,  | Ability to see distant objects clearly (farsightedness), but close objects are blurred. |
Astigmatism,  | Unevenness in the cornea, which results in visual distortion. |
| Presbyopia | A form of hyperopia that occurs as a normal process of aging. |
Conjunctiva,  | A transparent mucous membrane that covers the inner surfaces of the eyelids (the palpebral conjunctiva) and also extends over the sclera (bulbar conjunctiva), forming a pocket under each eyelid. Glands in the conjunctiva secrete mucus and tears. |
Sclera,  | Composed of collagen fibers meshed together to form an opaque structure commonly referred to as the "white" of the eye. The sclera forms a tough shell that helps protect the intraocular structures. |
| Cornea | The transparent and avascular cornea allows light to enter the eye. The curved cornea refracts (bends) in-coming light rays to help focus them on the retina. The cornea consists of five layers: the epithelium, Bowman's layer, the stroma, Descemet's membrane, and the endothelium. The epithelium consists of a layer of cells that helps protect the eye. Epithelial cells regenerate when damaged. The stroma consists of collagen fibrils. |
| Lacrimal Apparatus | Consists of the lacrimal gland and duscts, lacrimal canal and puncta, lacrimal sac, and nasolacrimal duct. In addition to the lacrimal gland, other glands provide secretons to make up the mucous, aqueous, and lipid layers of the tear film. The tear film moistens the eye and provides oxygen to the cornea. |
| Extraocular Muscles | Each eye is moved in three pairs of extraocular muscles: 1. Superior and inferior rectus muscles, 2. Medial and lateral rectus muscles, and 3. Superior and inferior oblique muscles. Neuromuscular coordination produces simultaneous movement of the eyes in the same direction (conjugate movement.) |
| Iris | The color of the eye. The structure has a small round opening in the center, the pupil, which allows light to enter the eye. The pupil constricts via action of the iris sphincter muscle (innervated by CNIII [occulomotor nerve]) and dilates via action of the iris dilator muscle (innervated by CN V [trigeminal nerve]) to control the amount of light that enters the eye. |
| Lens | A biconvex, avascular, transparent structure located behind the iris. It's supported by the anterior and posterior vviliary zonules. It bends light rays so that they fall onto the retina. Accommodation occurs when the eye focuses on a near object and is facilitated by contraction of the ciliary body, which changes the shape of the lens. |
| Ciliary Body | Consists of the ciliary muscles, which surrounds the lens and lie parallel to the sclera; the ciliary zonules, which attach to the lens capsule; and the ciliary processes, which constitute the terminal portion of the ciliary body. The ciliary processes lie behind the peripehral part of the iris and secrete aqueous humor. |
| Choroid | A highly vascular structure that serves to nourish the ciliary body, the iris, and the outer portion of the retina. It lies inside and parallel to the sclera and extends from the area where the optic nerve enters the eye to the ciliary body. |
Retina,  | The innermost layer of the eye that extends and forms the optic nerve. Neurons make up the major portion of the retina. Therefore retinal cells are unable to regenerate if destroyed. |
| Cochlear Implant Distortion | This is the way a cochlear implant sounds, 
|