| A | B |
|---|
| Nucleus | 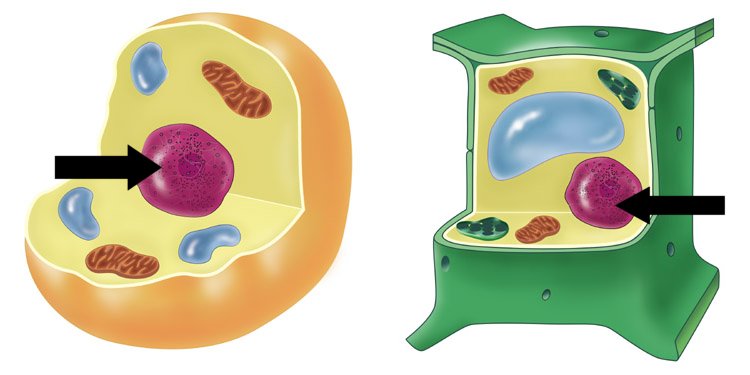 |
| Vacuole | 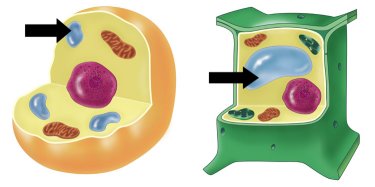 |
| Mitochondria | 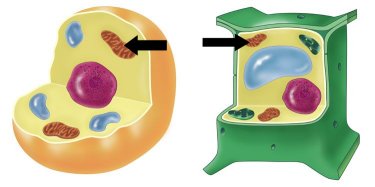 |
| Cell Membrane | 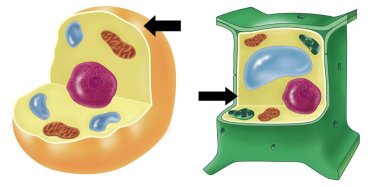 |
| Cytoplasm | 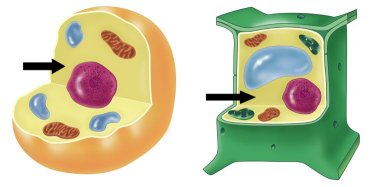 |
| Chloroplast | 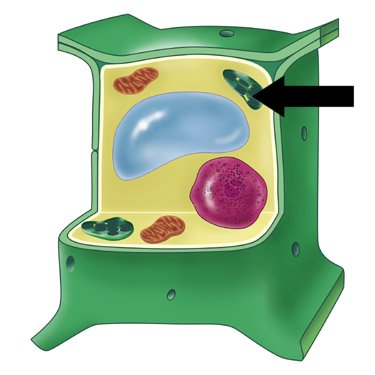 |
| Cell Wall | 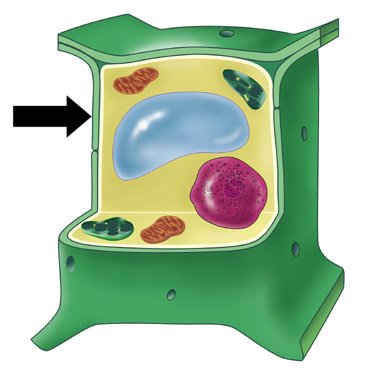 |
| Animal Cell | 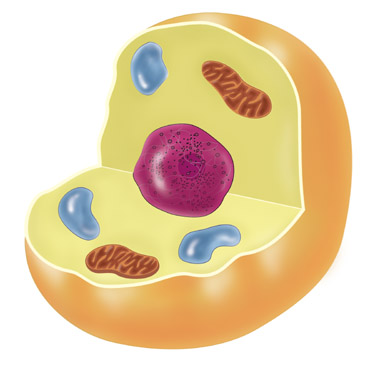 |
| Plant Cell | 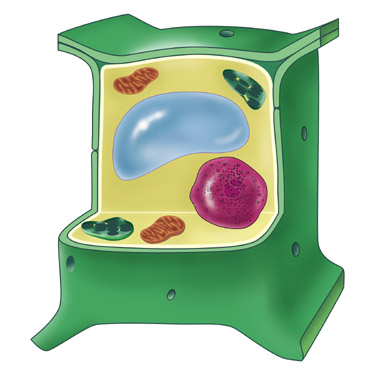 |
| Cell Membrane | A thin and flexible layer that surrounds all cells. It regulates what enters and leaves the cell, by allowing water and dissolved materials to pass into and out of the cell. |
| Cell Wall | The tough outer covering of a plant cell that protects, supports, and gives the cell its rigid shape. |
| Nucleus | The cell structure that controls all of a cell’s activities. |
| Cytoplasm | The jelly-like substance that fills much of the cell. |
| Chloroplast | The plant cell’s food factory. It is a structure in plant cells that captures light energy that is used in the food-making process. |
| Mitochondria | The powerhouse of the cell. It is where food is changed to energy. |
| Vacuole | A cell part that stores water, nutrients (food) and waste. |