| A | B |
|---|
Vascular plants,  | Plants that have a transport system. They can grow tall. |
nonvascular plants,  | These plants are small and have no transport systems. They grow close to the ground. |
seed plants,  | trees and flowering plants |
seedless plants,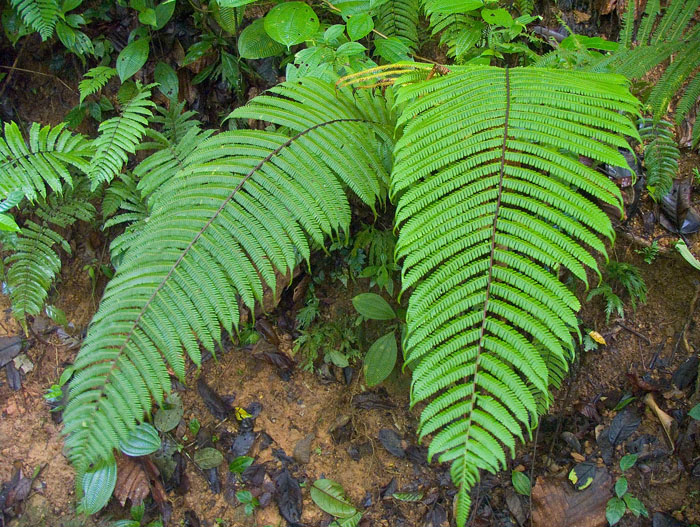  | Plants that produce no seeds. They produce spores that can dvelop into a new plant. |
gymnosperm,  | A seed plant that does not produce a flower. |
Angiosperm, 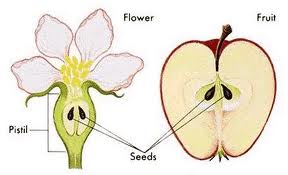 | A seed plant that produces flowers and fruit. |
Root, 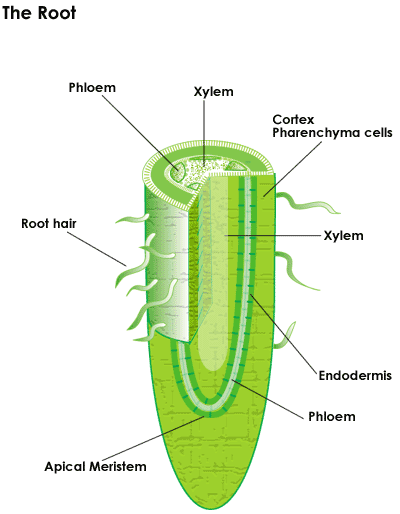 | part of a plant that absorbs water and minerals, stores food, and anchors the plant. |
Root hair,  | Threadlike projections from a plant root. |
Root cap,  | Covers the tip of the root. It protects the root tip as it pushes into the ground. |
| Epidermis | The outer layer of a root. It absorbs water. Also, the layer directly below the cuticle in the leaf and the underside of the leaf. |
Cortex,  | The layer in the root located just under the epidermis. Used to store food and nutrients. |
Aerial Roots,  | Never touch the ground. They anchor the plant to trees, rocks, or other surfaces. |
Fibrous roots, 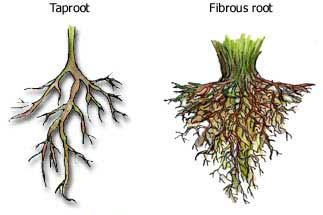 | Thin, branching roots. They cover a wide area. They don't go deep into the ground. |
Tap Roots,  | Single, main stalklike root. Grow deep into the ground. |
Prop Roots, 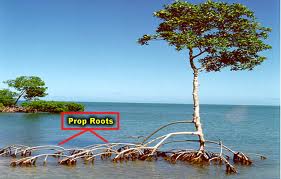 | Grow at the bottom of a plant's stem. They prop up and support the plant so it cannot be knocked over. |
Stems, 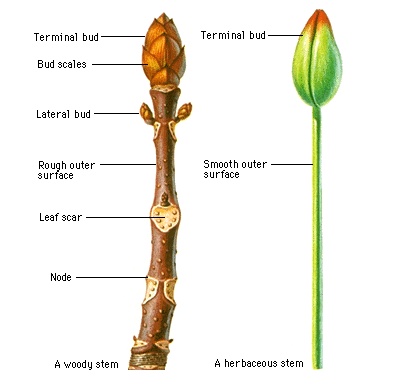 | Support structure and transport system for the plant. |
Woody stems,  | Stems covered in bark. Do not contain chlorophyll. |
Soft stems,  | Soft, green, and can bend. |
| Xylem | A series of tubes that moves water and minerals UP the stem. One direction transport system: only flows up from the plant's roots to the leaves. |
| Phloem | Tubes that move sugars that are made in the leaves to other parts of the plant. Two-way transport system: flows up and down. |
| Cambium | The layer that separates the xylem and phloem layers. Xylem and Phloem cells are produced here. |
Leaves,  | Their function is to carry out photosynthesis. |
Cuticle, 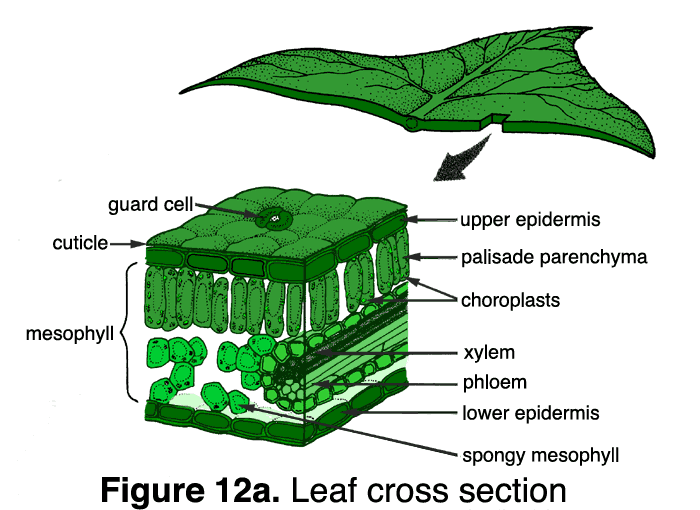 | The top waxy layer of a leaf. |
Stomata,  | Air enters and moves out of the plant through tiny pores on the underside of the leaves. A single opening is called a stoma. |
transpiration, 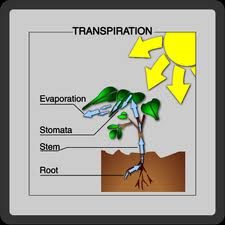 | The loss of water through a plant's leaves. |
Guard cells,  | They control the stoma to let excess water out, or to keep water in. |
| Cellular respiration | The process in which evergy is released from food (sugar) inside a plant's cell. |
conifers, 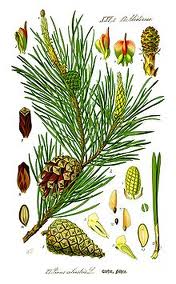 | Plants that produce cones. |
| annual | This type of plant completes its life cycle within a growing season. |
| perennial | This type of plant lives year after year, usually produing new growth and flowers during the spring. |
Photosynthesis,  | The process of making food. |