| A | B |
|---|
| colligative property | The property of a solution that depends on the number of particles of solute present; for example, freezing point depression |
| colloidal dispersion | A mixture in which the particles do not settle upon standing because they exhibit Brownian motion. |
| electrolyte | A compound that conducts an electrical current when dissolved in water |
| heterogeneous solution | A mixture that is not uniform in composition |
| homogeneous solution | A mixture that is uniform in composition |
| molarity | a measure of the concentration of a solution |
| moles | Calculated as M x V |
| saturated solution | A solution containing the maximum amount of solute for a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature. |
| solubility | the amount of a substance that dissolves in a given quantity of solvent at specified conditions of temperature and pressure to produce a saturated solution |
| solute | dissolved particles in a solution |
| solution | a homogeneous mixture; consists of solutes dissolved in a solvent |
| solvent | The dissolving medium in a solution |
| supersaturated solution | Crystallization of excess solute occurs on a rough surface or upon the addition of a seed crystal of solute. |
| suspension | a mixture from which some of the particles settle out slowly upon standing |
| unsaturated | a solution that contains less solute than a saturated solution at a given temperature |
| acid | A compound that ionizes in water to produce H+ ions; pH < 7 |
| acidic | any solution with a pH < 7 |
| alkaline | a basic solution |
| amphoteric | A substance that acts as both an acid and a base |
| Arrehenius Acid | a compound that produces a hydrogen ion (H+) when dissolved in water |
| Arrehenius Base | a compound that produces a hydroxide ion (OH-) when dissolved in water (H+) |
| base | A compound that ionizes in solution to produce OH-; pH > 7 |
| basic | any solution with a pH > 7 |
| Bronsted-Lowry Acid | Acid/base theory that describes a substance as a proton (H+) donor |
| Bronsted-Lowry Base | Acid/base theory that describes a substance as a proton (H+) acceptor |
| buffer | A solution in which the pH remains relatively constant when small amounts of acid or base are added |
| conjugate acid | the particle formed when a base gains a hydrogen ion; NH4+ is the conjugate acid of the base NH3 |
| conjugate acid-base pair | two substances that are related by the loss or gain of a single hydrogen ion; ammonia (NH3) and the ammonium ion (NH4+) are a conjugate acid-base pair |
| conjugate base | the particle that remains when an acid has donated a hydrogen ion; OH- is the conjugate base of the acid water |
| diprotic acid | an acid with two H+ ionsany acid that contains two ionizable protons (hydrogen ions); sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is a diprotic acid |
| electron pair acceptor | a Lewis acid |
| electron pair donor | a Lewis base; a substance with a nonbonding pair of electrons |
| hydrogen ion acceptor | a Bronsted-Lowry base |
| hydrogen ion donor | a Bronsted-Lowry acid |
| hydronium ion | H+ ion |
| hydroxide ion | OH- ion |
| indicator | A substance that indicates the degree of acidity or basicity of a solution through characteristic (usually by a change in color) |
| Lewis Acid | an electron pair acceptor |
| Lewis Base | an electron pair donor |
| litmus | A water-soluble blue powder that changes to red with increasing acidity and to blue with increasing basicity |
| monoprotic acid | any acid that contains one ionizable proton (hydrogen ion); nitric acid (HNO3) is a monoprotic acid |
| neutral | an aqueous solution in which the concentrations of hydrogen and hydroxide ions are equal; it has a pH of 7.0 |
| neutralization | A reaction in which an acid and a base react to form a salt and water |
| pH | – log [H+]; a number used to denote the hydrogen-ion concentration, or acidity, of a solution |
| pOH | – log [OH-]; a number used to denote the hyroxide-ion concentration of a solution |
| phenopthalein | chemical indicator that is clear in an acidic solution, but turns pink in a basic solution |
| strong acid | An acid that completely ionizes in aqueous solution; for example, hydrochloric acid, HCl. |
| strong base | A base that completely ionizes in aqueous solution; for example, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) |
| titration | Volumetric analysis used to determine the concentration of an acid using a base of known concentration |
| triprotic acid | any acid that contains three ionizable protons (hydrogen ions); phosphoric acid (H3PO4) is a triprotic acid |
| weak acid | an acid that is only slightly ionized in aqueous solution |
| weak base | an base that is only slightly ionized in aqueous solution |
| percent solution (w/w) | w-w, 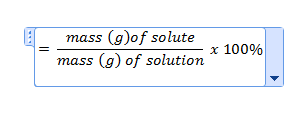 |
| percent solution (w/v) | w-v, 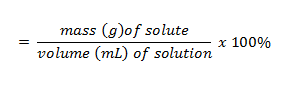 |
| percent solution (v/v) | v-v, 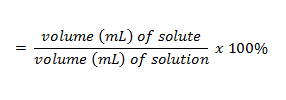 |