| A | B |
|---|
| Axial Tilt | Is the angle between an object's rotational axis and a line through the centre of the object perpendicular to its orbital plan, 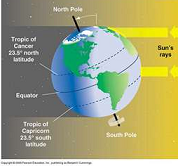 |
| Cold Front | The boundary formed when a cool air mass pushes into and under a warm air mass., 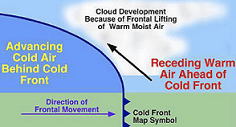 |
| Discontinuity | A surface at which seismic wave velocities change.,  |
| Extrusive Igneous Rocks | Rock that forms by the freezing of lava above ground, after it flows or explodes out onto the surface and comes into contact with the atmosphere or ocean., 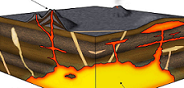 |
| Giant star | A very bright star of large diameter and low density (relative to the Sun).,  |
| Jupiter | The fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System.,  |
| Mars | The fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars.,  |
| Non-Renewable | Cannot be replenished (made again) in a short period of time,  |
| Plate Tectonics | The theory that Earth’s crust is broken up into a number of large pieces, or plates, that move and interact, producing many of Earth’s surface features.,  |
| Reflecting Telescope | A telescope in which light from the object is gathered and focused by a concave mirror, with the resulting image magnified by the eyepiece., 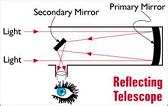 |
| Secondary Wave | A transverse seismic wave., 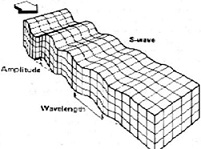 |
| Solar Winds | Streams of electrically charged particles flowing at high speeds from the sun's corona.,  |
| Thermal Pollution | An increase in the temperature of a body of water, caused by human activities, that may be harmful to living things in that environment.,  |
| Universe | The totality of known or supposed objects and phenomena throughout space; the cosmos; macrocosm.,  |
| Weathered | Seasoned or otherwise affected by exposure to the weather.,  |