 |
Java Games: Flashcards, matching, concentration, and word search. |
 |
 |
| A | B |
|---|
| Bedrock | The unbroken, solid rock portion of Earth's crust,  |
| Composite Volcano | Sometimes called stratovolcanoes, are typically deep-sided, symmetrical cones of large dimension built of alternating layers of lava flows, volcanic ash, cinders, blocks, and bombs and may rise as much as 8,000 ft above their bases., 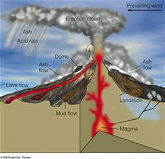 |
| Drainage Basin | A drainage basin is an extent of land where water from rain and melting snow or ice drains downhill into a body of water, such as a river, lake, reservoir, estuary, wetland, sea or ocean.,  |
| Faulting | The process in which internal forces cause Earth’s crust to break and slide along a fracture called a fault., 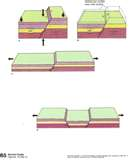 |
| Graphite | A form of the element carbon in which carbon atoms form flat layers., 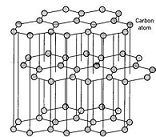 |
| Latent Heat | The quantity of heat absorbed or released by a substance undergoing a change of state, such as ice changing to water or water to steam, at constant temperature and pressure. Also called heat of transformation., 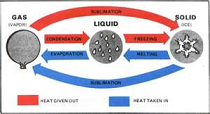 |
| Metamorphic Rock | A rock produced igneous & sedimentary rock go through change by heat, pressure, or both.,  |
| Nuclear Reactor | Is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. The most common use of nuclear reactors is for the generation of electrical power and for the power in some ships. This is usually accomplished by methods that involve using heat from the nuclear reaction to power steam turbines., 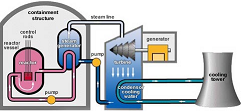 |
| Pluto | A dwarf planet that until 2006 was classified as the ninth planet in our solar sytem, having a sidereal period of revolution about the sun of 248.5 years, 4.4 billion kilometers (2.8 billion miles) distant at perihelion and 7.4 billion kilometers (4.6 billion miles) at aphelion, and a diameter less than half that of Earth.,  |
| Regolith | The layer of rock and mineral fragments that rests on bedrock and is produced by the weathering of rocks. Regolith constitutes the surface of most land.,  |
| Sediment | Material that settles to the bottom of a liquid; lees. Solid fragments of inorganic or organic material that come from the weathering of.,  |
| Spectroscope | Is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum., 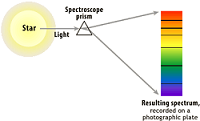 |
| Tide | The periodic variation in the surface level of the oceans and of bays, gulfs, inlets, and estuaries, caused by gravitational attraction of the moon and sun.,  |
| Uranus | The planet seventh in order from the sun, having an equatorial diameter million miles (2,871 million km), a period of revolution of 84.07 years, and 15 moons.of 32,600 miles (56,460 km), a mean distance from the sun of 1,784,  |
| Westerlies | The Westerlies, anti-trades or Prevailing Westerlies, are the prevailing winds in the middle latitudes between 35 and 65 degrees latitude, blowing from the high pressure area in the horse latitudes towards the poles., 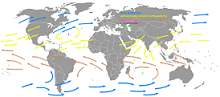 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
| |