| A | B |
|---|
| Absolute Dating | The determination of the age of an object with reference to a specific time scale., 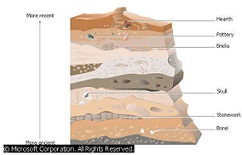 |
| Biogeochemical Cycle | Transport and transformation of chemicals in ecosystem,, 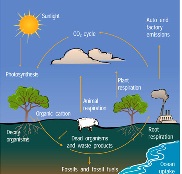 |
| Constellation | Group of celestial bodies (usually stars) that can create a pattern in the sky,  |
| Earthquake | A shaking or vibrating of Earth’s crust, usually caused by the sudden movement of rocks sliding along a fault.,  |
| Folding | A bend in rock strata or in any planar feature,  |
| Greenhouse Effect | An atmospheric heating phenomenon, caused by short-wave solar radiation being readily transmitted inward through the earth's atmosphere but longer-wavelength heat radiation less readily transmitted outward, owing to its absorption by atmospheric carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and other gases; thus, the rising level of carbon dioxide is viewed with concern., 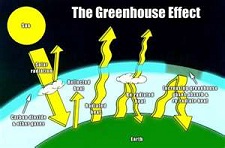 |
| Lee Rain Shadow | A region in the lee of mountains that receives less rainfall than the region windward of the mountains., 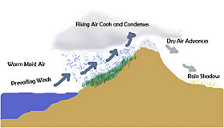 |
| Meteoroid | A sand-to boulder-sized particle of debris in the Solar System.,  |
| Ocean | The vast body of salt water that covers almost three fourths of the earth's surface.,  |
| Pollutants | Harmful substances that contaminate the environment, often produced by human activities.,  |
| Relative Dating | In archaeology, the arrangement of artifacts or events in a sequence relative to one another but without ties calendrically measured time; the arrangement of artifacts in a typological sequence or serration.,  |
| Seismic Wave | A seismic wave is an elastic wave generated by an impulse such as an earthquake or an explosion., 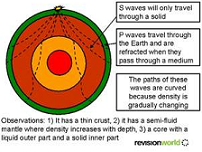 |
| Star | Any of the heavenly bodies, except the moon, appearing as fixed luminous points in the sky at night.,  |
| Time Zone | A time zone is a region of the earth that has uniform standard time, usually referred to as the local time. By convention, time zones compute their local time as an offset from UTC (see also Greenwich Mean Time). Local time is UTC plus the current time zone offset for the considered location., 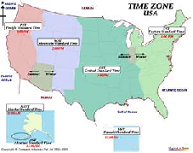 |
| Van Allen Belts | Two donut- shaped regions 1,000- 25,000 kilometers above earth that contain electrons and protons traveling at high speeds, 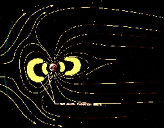 |
| Wind | The movement of air over earths surface.,  |