| A | B |
|---|
| Agricultural | Of, relating to, used in, or concerned with agriculture,  |
| Burden | A disadvantage to a person or society of a technological device or process.,  |
| Computer Network | A group of computers connected by cables or telephone lines.,  |
| Controls | To verify or regulate a scientific experiment by conducting a parallel experiment or by comparing with another standard,  |
| Experiment | A tentative procedure or policy,  |
| Graduated Cylinder | A container for liquid with a wider base gradually narrowing to the top and marked with a graded scale; also called graduated flask,  |
| Independent Variable | The variable value is changed; the experiment value is not affected at any time. So we can say that variable is the independent variable. For example, if you open a faucet (the independent variable), the quantity of water flowing (dependent variable) changes in response--you observe that the water flow increases. The number of dependent variables in an experiment varies, but there is often more than one., 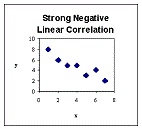 |
| Laser | A device that produces coherent light,  |
| Meter Stick | A ruler one meter long (usually marked off in centimeters and millimeters),  |
| Periodic Table | An arrangement of the elements in order of atomic number, in which elements with similar properties are grouped in columns., 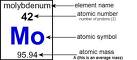 |
| Random | Proceeding, made or occurring without definite aim.,  |
| Science | Knowledge or a system of knowledge covering general truths or the operation of general laws especially as obtained and tested through the scientific method and concerned with the physical world and its phenomena.,  |
| Solenoid | Is a coil wound into a tightly packed helix. In physics, the term solenoid refers to a long, thin loop of wire, often wrapped around a metallic core, which produces a magnetic field when an electric current is passed through it.,  |
| Theory of Evolution | Evolution is the change in the inherited traits of a population of organisms through successive generations. When a population splits into smaller groups, these groups evolve independently and develop into new species,  |
| Vary Inversely | A term used to describe the relationship between two variables whose graph forms a curve that slopes downward from left to right.,  |