| A | B |
|---|
| Newton's First Law of Motion | An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. An object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This law is often called ?"the law of inertia",  |
| Average Speed | The average distance traveled per hour; the distance traveled divided by the time taken, 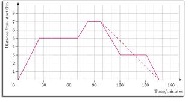 |
| Chemical Energy | Energy released from a substance, or absorbed in the formation of a chemical compound, during a chemical reaction., 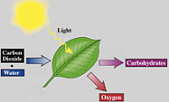 |
| Convection | The transfer of heat through a fluid (liquid or gas) caused by molecular motion,  |
| Electrical Potential | At a point in space is the electrical potential energy divided by charge associated with a static (time-invariant) electric field., 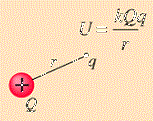 |
| Flammable | Capable of catching fire and burning easily.,  |
| Heat | The movement of thermal energy from one substance to another.,  |
| Insulation | Material used to reduce or slow the flow of heat from one area to another., 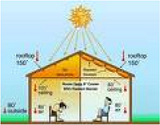 |
| Longitudinal wave | A wave that moves the medium parallel to the direction in which the wave travels., 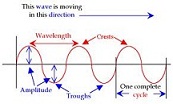 |
| Molecule | Is defined as an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms in a definite arrangement held together by very strong (covalent) chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from polyatomic ions in this strict sense., 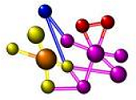 |
| Oxidation Number | The oxidation number is the electrical charge that the central atom in a coordination compound would have if all the ligands and electron pairs were removed. Usually the oxidation number has the same value as the oxidation state.,  |
| Pressure | Pressure is a measure of the force applied over a unit area. Pressure often is expressed in units of Pascal’s or pounds per square inch. In equations, pressure is denoted by the symbol 'P'.,  |
| Semiconductor | A substance that can conduct electricity under some conditions.,  |
| Strong Force | Also called nuclear force. the short-range attractive force between baryons that holds together the nucleus of the atom.,  |
| Ultrasound | Sound waves with frequencies above 20,000 Hz.,  |
| X- Rays | Electromagnetic waves with higher frequencies than ultraviolet rays, but shorter than gamma rays, 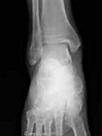 |