| A | B |
|---|
| Applications of Nuclear | Ways to use nuclear energy. One way is to use the nuclear energy for electricity to power homes and businesses,  |
| Centripetal Acceleration | Centripetal acceleration points toward the center of the circular path, but is felt as a force pushing to the outer edge of the circular path., 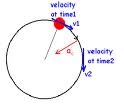 |
| Concentration | The amount of one material dissolved in a given amount of another material., 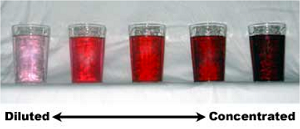 |
| Ductile | A term used to describe a material that can be pulled out into a wire,  |
| Energy Conversion | The process of changing one form of energy to another, 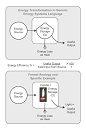 |
| Gears | Two or more wheels linked together by interlocking teeth.,  |
| Indicator | A compound that changes colors when in contact with an acid or a base, 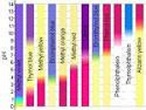 |
| Law of Conservation of Matter | During an ordinary chemical change, there is no detectable increase or decrease in the quantity of matter.,  |
| Melting Point | The temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid.,  |
| Nuclear Radiation | Particles and energy produced during radioactive decay.,  |
| Polar Molecule | A molecule in which the centroid of the positive charges is different from the centroid of the negative charges., 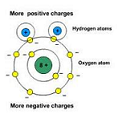 |
| Regular Reflection | Reflection that occurs when parallel rays of light hit a smooth surface and all reflect at the same time, 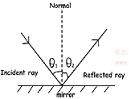 |
| Speed | Rapidity in moving, going, traveling, proceeding, or performing; swiftness; celerity the speed of light; the speed of sound,  |
| Tracer | A radioactive isotope that can be followed through the steps of a chemical reaction or industrial process,  |
| Wave | A disturbance that transfers energy from place to place.,  |