| A | B |
|---|
| Atomic Mass | The average mass of one atom of an element,  |
| Chain Reaction | A multistage nuclear reaction, especially a self-sustaining series of fissions in which the release of neutrons from the splitting of one atom leads to the splitting of others., 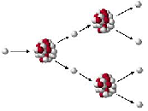 |
| Conduction | The transfer of heat between two parts of a stationary system, caused by a temperature difference between the parts., 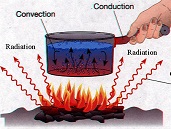 |
| Electric Charge | Is a physical quantity of matter which causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter.Either positive or negative, 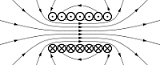 |
| Ester | An chemical compound made by chemically combining an alcohol and an organic acid., 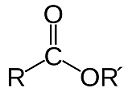 |
| Gravitational Potential Energy | Potential energy that depends on the height of an object., 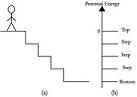 |
| Inertia | The tendency of a body to resist acceleration; the tendency of a body at rest to remain at rest or of a body in straight line motion to stay in motion in a straight line unless acted on by an outside force.,  |
| Laws of Motion | The three laws proposed by Sir Isaac Newton to define the concept of a force and describe motion, used as the basis of classical mechanics.,  |
| Metalloid | An element that has some of the characteristics of metals and some of the characteristics of nonmetals, .jpeg) |
| Ohm’s Law | The current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference or voltage across the two points, and inversely proportional to the resistance between them.,  |
| Polymer | Large, complex molecule built from smaller molecules bonded together., 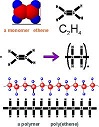 |
| Resonance | Term in chemistry used to explain properties of the octet rule when a single Lewis structure is inadequate., 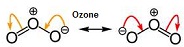 |
| State of Matter | The three forms (liquid, solid, gas) in which matter exists, 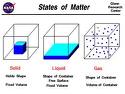 |
| Transformer | An electrical device by which alternating current of one voltage is changed to another voltage,  |
| Weak Base | A chemical base that does not ionize fully in an aqueous solution. Ammonia is an example of a weak base.,  |
| Atomic Mass Unit (AMU) | A unit of measurement for the mass of particles in atoms, 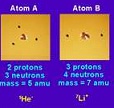 |