| A | B |
|---|
| Atomic Theory | A theory of the structure of the atom, 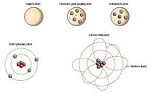 |
| Chemical Bond | The force that holds two atoms together., 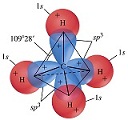 |
| Conservation of Mass | The principle stating that charges are neither created nor destroyed., 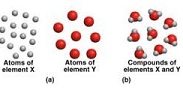 |
| Electric Meter | A meter for measuring the amount of electric power used,  |
| Ferromagnetic Material | A material that is strongly attracted to a magnet, and which can be made into a magnet, 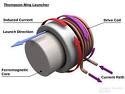 |
| Group | Elements in the same vertical column of the periodic table; also called a family,  |
| Inhibitor | Substance that retards or stops a chemical reaction.,  |
| Lipid | An energy- rich compound made of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen; fats, oils, waxes, and cholesterol are lipids,  |
| Mixture | Two or more substances that have been combined such that each substance retains its own chemical identity., 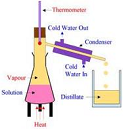 |
| Organic Acid | A substitute hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboxyl groups (-COOH) of atoms, 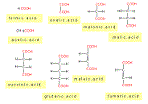 |
| Potential Energy | The energy possessed by a body as a result of its position or condition rather than its motion.,  |
| Saturated Solution | Mixture that contains as much solute in it as possible at a given temperature.,  |
| Step Up Transformers | A transformer that increases voltage from primary to secondary (more secondary winding turns than primary winding turns, 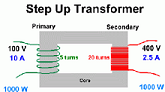 |
| Transverse Waves | A wave that moves the medium in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels, 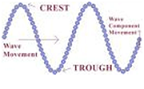 |
| Wheel and Axle | A simple machine consisting of two circular or cylindrical objects that are fastened together and rotate about a common axis.,  |