| A | B |
|---|
| Amplitude Modulation | Technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave., 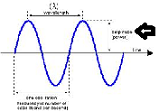 |
| Carbohydrate | An energy - rich organic compound made of The elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen., 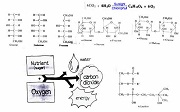 |
| Compound Machine | Any combination of simple machines working together.,  |
| Dissonance | The sound produced when notes that have no musical relationship are played together,  |
| Electron Dot Diagram | A diagram that uses dots to represent an element's valence electrons., 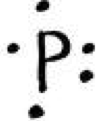 |
| Fullerene | A form of the element carbon that consists of carbon atoms arranged in a repeating pattern similar the surface of a soccer ball,  |
| Ideal Mechanical Advantage | Is a force-amplifying effectiveness of a simple machine (lever, wedge, wheel and axle, pulley, or screw). The theoretical mechanical advantage of a system is the ratio of the force that performs the useful work to the force applied, assuming there is no friction in the system. In practice, the actual mechanical advantage will be less than the theoretical value by an amount determined by the amount of friction., 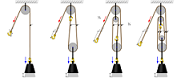 |
| Kelvin | Is a unit of measurement for temperature.,  |
| Mechanical | Being a machine; operated by machinery,  |
| Non-Metals | Are the elements in groups 14-16 of the periodic table.,  |
| Pigment | Dry coloring material (especially a powder to be mixed with a liquid to produce paint, etc.),  |
| Reactant | Any substance that undergoes a chemical change in a given reaction.,  |
| Solvent | A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances, 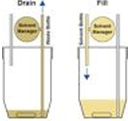 |
| Thermal Energy | The total energy of a substance's particles due to their movement or vibration.,  |
| Volt | The volt (symbol V) is the SI derived unit of electromotive force, commonly called "voltage". It is also the unit for the related but slightly different quantity electric potential difference (also called "electrostatic potential difference").,  |