| A | B |
|---|
| Newton's Second Law of Motion | Acceleration is produced when a force acts on a mass. The greater the mass (of the object being accelerated) the greater the amount of force needed (to accelerate the object)., 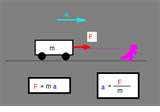 |
| Balance (Equilibrium) | A state of bodily equilibrium,  |
| Chemical Equation | Short, easy way to show a chemical reaction, using symbols instead of words., 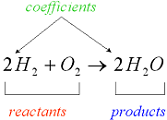 |
| Convection Current | A current caused by the rising of heated fluid and sinking of cooled fluid.,  |
| Electrical Power | The product of voltage and current.,  |
| Fluid | Any substance that can flow and easily change shape.,  |
| Heat Energy | A form of energy that is transferred by a difference in temperature,  |
| Insulator | A material that does not easily transfer thermal energy or electric current between its particles,  |
| Loudness | Perception of the intensity of a sound., 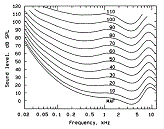 |
| Momentum | Force or speed of movement; impetus, as of a physical object or course of events.,  |
| Oxyanion | Is a chemical compound with the generic formula AxOyz, 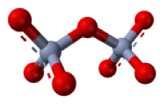 |
| Prism | A polyhedron with two congruent and parallel faces (the bases) and whose lateral faces are parallelograms, and made of glass or quartz; used to deviate a beam or invert an image., 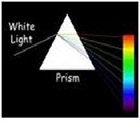 |
| Separation | An act or instance of separating or the state of being separated.,  |
| Structural Formula | A description of a molecule that shows the kind, number, and arrangement of atoms, 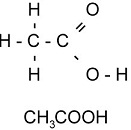 |
| Ultraviolet Rays | Electromagnetic waves with frequencies higher than visible light, but lower than x- rays., 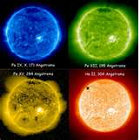 |