| A | B |
|---|
| Atomic Nucleus | The center of an atom.,  |
| Charging by Induction | The generation of electromotive force in a closed circuit by a varying magnetic flux through the circuit.,  |
| Conservation of Charge | The law that states that charges are neither created nor destroyed., 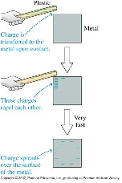 |
| Electric field | Surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields., 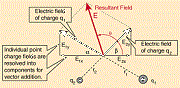 |
| External Combustion Engine | An engine powered by fuel burned outside the engine,  |
| Grounded | Term used to describe a circuit that allows charges to follow directly from the circuit to the ground connection, 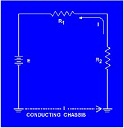 |
| Infrared Rays | Electromagnet radiation having wavelength above microwave but below visible light: Given off and absorbed by all bodies at above the absolute-zero temperature., 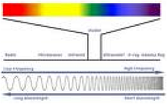 |
| Lever | A rigid bar that pivots about one point and that is used to move an object at a second point by a force applied at a third., 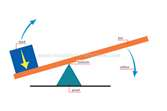 |
| Microwave | Super high frequency (SHF) Frequency band between 3 GHz and 30 GHz. So desiganted by Federal Communications Comission.,  |
| Optical Fiber | Long, thin strand of glass or plastic that can carry light for long distances without allowing light to fade out; can be used for transmitting messages., 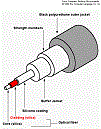 |
| Potential Difference | The difference in electrical charge between two points in a circuit expressed in volts, 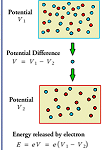 |
| Salt | An ionic compound that can form from the neutralization of an acid with a base, .jpeg) |
| Static Friction | Friction between two objects in contact that are not moving. Static friction is generally greater than kinetic friction and must be overcome before an object can be set in motion., 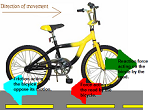 |
| Translucent | Term used to describe a material that scatters light as it passes through.,  |
| Weight | The amount or quantity of heaviness or mass; amount a thing weighs., 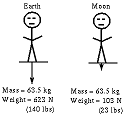 |
| Atomic Number | Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element.,  |