| A | B |
|---|
| Aurora | Glowing region produced by the interaction of changed particles from the sun and atoms in the atmosphere,  |
| Chemical Change | A change that occurs when one or more substances change into entirely new substances with different properties., 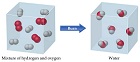 |
| Conservation of Matter | A fundamental principle of classical physics that matter cannot be created or destroyed in an isolated system,  |
| Electric Motor | A device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.,  |
| Filter | Designed to physically block certain objects or substances while letting others through,  |
| Half-life | The length of time for half the atoms of a radioactive isotope sample to decay, 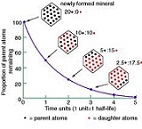 |
| Input Force | It is the force you put into something input force force exerted on a machine.,  |
| Liquid | A state of matter that has a definite volume but no definite shape.,  |
| Model | A synthetic coordination entity that closely approaches the properties of a metal ion in a protein and yields useful information concerning biological structure and function.,  |
| Organic Compounds | Most compounds that contain carbon., 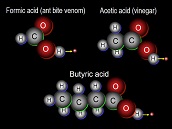 |
| Potential Power | Energy that is stored and held in readiness., 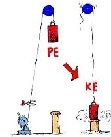 |
| Screw | Simple machine that consists of an inclined plane wrapped around a central cylinder to form a spiral,  |
| Strong Acid | Is an acid that ionizes completely in an aqueous solution by losing one proton.,  |
| Trough | The lowest part of a transverse wave, 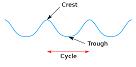 |
| Work | The product of force and distance when a force is used to move an object., 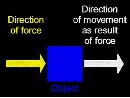 |