| A | B |
|---|
An angle less than 90 degrees, 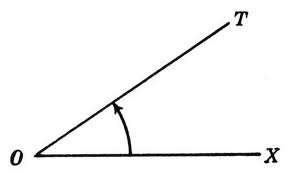 | Acute angle |
A 90 degree angle, 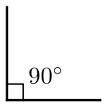 | Right angle |
The sum of two angles is 180 degrees, 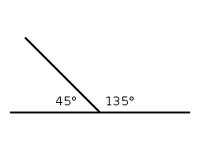 | Supplementary angle |
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees, 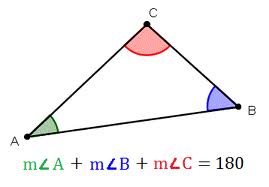 | Triangle Sum Theorem |
A triangle with two equal sides,  | Isosceles triangle |
A triangle with three equal sides, 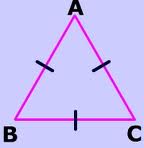 | Equilateral triangle |
A triangle with all different side lengths,  | Scalene triangle |
Two angles that share a ray/side and a vertex/point, 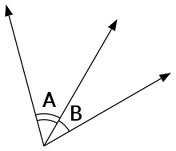 | Adjacent angles |
Two lines that interact at 90 degrees, 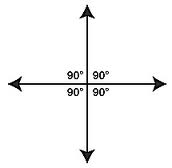 | Perpendicular lines |
An angle that is 180 degrees, 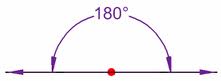 | Straight angle |
Two identical figures, 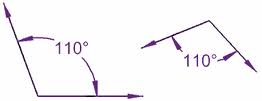 | Congruent figures |
Formed by two rays with a common vertex/point., 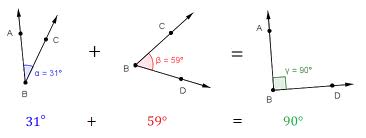 | angle |
An angle that is greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees, 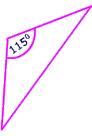 | Obtuse angle |
Two angles whose sum is 90 degrees, 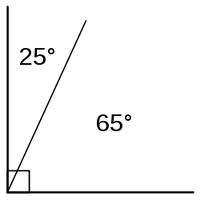 | Complementary angles |
Two lines on a plane that never interset, 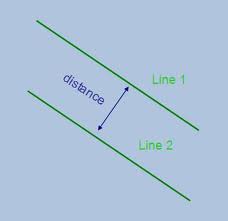 | Parallel lines |
A line that intersects two or more lines that lie in the same plane, 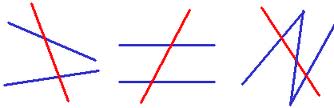 | Transversal |
The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side, 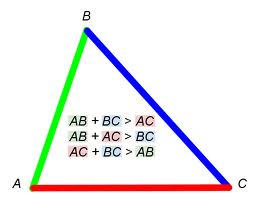 | Triangle Inequality Theorem |
The point that divides a segment into two congruent segments, 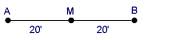 | Midpoint |
A way of matching up two sets of figures,  | Correspondence |
A change in a figure's position,  | Transformation |
A figure that slides along the line without turning, 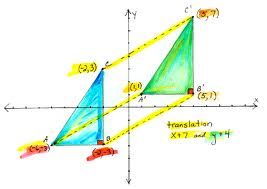 | Translation |
A figure that flips across a line, 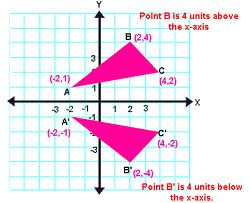 | Reflection |
A figure that turns, 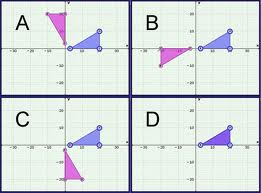 | Rotation |
A point that a figure is turned on, 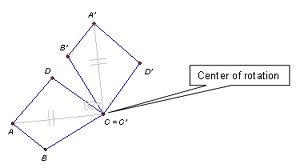 | Center of rotation |
The result of a transformation, translation, reflection or rotation,  | Image |
Transformation that results in a same size image, 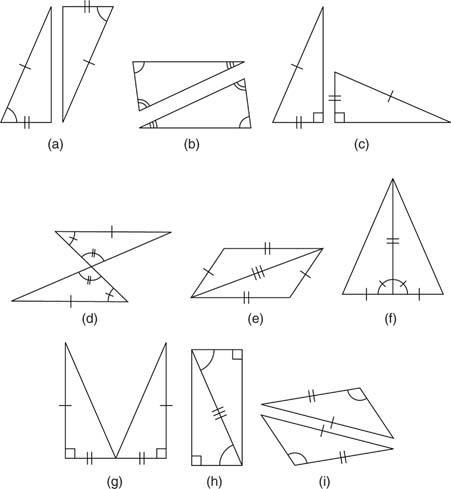 | Congruence transformation |
Transformation that results in a similar image,  | Similarity transformation |
A triangle with three acute angles, 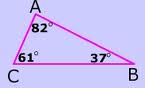 | Acute triangle |
Two angles that are equal,  | Congruent angles |
A triangle with a right angle, 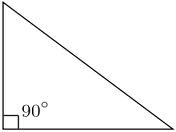 | Right triangle |
Two angles that share a common vertex and same measurement, 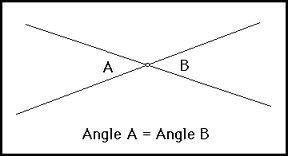 | Vertical angles |