| A | B |
|---|
| The scientific study of the interactions between organisms and the environment is called _____. | ecology p. 1144 |
| The windward side of a mountain range is usually ______ than the leeward side which is usually ____ due to the _____ effect | moister, drier, rainshadow effect p. 1148,  |
| The upper part of an aquatic biome, where enough light penetrates for photosynthesis to occur, is called the ____. | photic zone p. 1157,  |
| The lower layer of an aquatic ecosystem, which doesn't receive enough light to support photosynthesis, is called the _____ . | aphotic zone p. 1157,  |
The bottom substrate of all aquatic ecosystems is called the ____ zone and the organisms that live there are called the ____.,  | benthic zone, benthos pp. 1157 and 1162,  |
| The zone of open water that includes both the photic and aphotic zone is called the _____ zone. | pelagic p. 1157,  |
The pond in the picture below is classified as being ______ because of its murky (turbid) nutrient ____ water that supports a lot of life (especially algae).,  | eutrophic, nutrient-rich p. 1159,  |
The lake in the picture below is classified as being ____ because of its clear nutrient ____ waters that support little photosynthetic life.,  | oligotrophic, nutrient-poor p. 1159,  |
Which biome is shown in the picture below?,  | coral reef p. 1162,  |
| _____ largely determines the distribution and structure of terrestrial biomes. | Climate (mostly temperature and precipitation) pp. 1150-1151 |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | Tropical forest (The map shows the distribution of tropical forests. The picture is a tropical rainforest in Borneo) p. 1153,  |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | Chaparral p. 1154,  |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | Northern coniferous forest p. 1155, 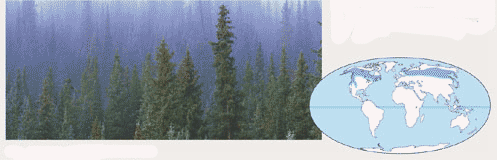 |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | Desert p. 1153,  |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | Savanna p. 1154,  |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | Temperate broadleaf forest (a.k.a. Temperate Deciduous Forests) p. 1156,  |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | Temperate grasslands p. 1155,  |
Which biome is pictured below?,  | tundra p. 1156,  |
| Which terrestrial biome has the greatest biodiversity? | Tropical forests (biodiversity refers to the number of different species that can be found in an area) p. 1153 |
| Which biome is very warm with a dry season that can last eight or nine months? | savanna p. 1154,  |
| Which biome is usually found close to the coast and has mild rainy winters and long dry summers? | chaparral p. 1154,  |
| Which biome is characterized by short drought resistant trees and shrubs? | chaparral p. 1154,  |
| Which biome is characterized by cold dry winters and hot humid summers? | temperate grasslands p. 1155,  |
| Deciduous trees are trees that ______. | drop their leaves in the fall p. 1156,  |
| Which biome is characterized by a layer of permafrost just below the surface soils? | Tundra p. 1156,  |
| The tundra is characterized by a permanently frozen layer of soil just below the surface called _____. | permafrost p. 1156,  |
| A biome located throughout midlatitude regions where there is sufficient moisture to support the growth of large, broadleaf deciduous trees. | temperate broadleaf forest p. 1156,  |
| Which biome is characterized by sparsely scattered individual trees and large herds of herbivores, large carnivores, and occasional fires and droughts? | savanna p. 1154,  |
| A warm-water, tropical ecosystem dominated by the hard skeletal structures secreted primarily by the resident cnidarians. | Coral reef (The cnidarians they are talking about are hard corals like the brain coral pictured below. Notice the white patch of calcium carbonate skeleton that is exposed where the coral polyps have died) p. 1162,  |
| A scrubland biome of dense, spiny evergreen shrubs found at midlatitudes along coasts where cold ocean currents circulate offshore; characterized by mild, rainy winters and long hot dry summers. | chaparral p. 1154,  |
| The most significant influence on the distribution of organisms is _____. | climate p.1144 |
| ______ is the long-term prevailing weather conditions in a given area. | Climate p. 1144 |
| The _____ is the global ecosystem - the sum of all the planet's ecosystems and landscapes. | biosphere p. 1145 |
| A(n) ______ is the community of organisms in an area and the physical factors with which those organisms interact. | ecosystem p. 1145 |
| A(n) ____ is a group of populations of different species in an area. | community p. 1145 |
| A(n) ____ is a group of individuals of the same species living in an area. | population p. 1145 |
| The living factors in an environment are called ____ factors. | biotic p. 1149 |
| The non-living factors in an environment are called ____ factors. | abiotic p. 1149 |
| _______ are major life zones characterized by vegetation type (in terrestrial ones) or physical environments (in aquatic ones). | Biomes p. 1150 |
| ______ biomes are aquatic biomes with salt concentrations somewhere around 3% while _____ biomes have salt concentrations near or below 0.1%. | Marine, freshwater p. 1157 |
| Any organism that is not strong enough to swim against the current (and therefore basically floats and drifts) is referred to as ______. If they are photosynthetic, they are called _____. If they are heterotrophs, they are referred to as ____. | plankton, phytoplankton, zooplankton (1159-1161),  |