| A | B |
|---|
| A liquid that has a uniform mixture of two or more substances is know as a(n) ___. | solution p.50 |
| In a glass of salt water, the ___ would be the solvent. | water p.50 |
| In a glass of salt water, the ___ would be the solute. | salt p.50 |
| In a solution of sugar and water, the sugar would be the ___. | solute p.50 |
| In a solution of sugar and water, the water would be the _____. | solvent p.50 |
| Acidic solutions have a pH that is ____ seven. | below pp.53&54 |
| Basic solutions have a pH that is ___ seven. | above pp.53&54 |
| Distilled water has a pH of ___. | seven pp.53&54 |
| A liquid with a pH of 1 would be described as being ___ than a liquid with a pH of 5. | more acidic pp.53&54 |
| A liquid with a pH of 6 would be described as being ___ than a liquid with a pH of 2 | less acidic pp.53&54 |
| A liquid with a pH of 8 would be described as being ___ than a liquid with a pH of 14. | less basic pp.53&54 |
| A liquid with a pH of 13 would be described as being ___ than a liquid with a pH of 7.8. | more basic pp.53&54 |
| As temperature ____, particles move faster and faster | increases p.48 |
| As temperature ____ particles move slower and slower. | decreases p.48 |
| Bonds in which the electrons between two atoms are shared about equally (because both atoms have similar electronegativities) are called _____. | nonpolar covalent bonds p.39 |
| Bonds in which the electrons between two atoms are not SHARED equally (because one atom has a significantly higher electronegativity) are called _____. | polar covalent bond p.46 |
| Bonds in which electrons aren't shared at all (because one atom has a MUCH higher electronegativity than the other) are called ______. | ionic bonds p. 40 |
| A weak attraction between hydrogen in one molecule and either an oxygen or nitrogen atom in another molecule is called a(n) _____. | hydrogen bond p.40 |
| Because oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, the electrons of the polar covalent bonds in a water molecule spend more time closer to the _______ atom, giving it a partial _____ charge. | oxygen, negative p.46 |
| The hydrogen atoms in a water molecule have a _____ _____ charge. | partial positive charge p.46 |
| Molecules in which the overall charge is unequally distributed, leading to parts of the molecule having a partial positive charge while other parts have a partial negative charge (like water) are called ______. | polar molecules p.46 |
| The extraordinary qualities of water are _______ properties resulting from the ______ bonding that orders molecules into a higher level of structural organization. | emergent, hydrogen p.47 |
Why is it unlikely that two neighboring water molecules would arrange themselves like the ones shown below?,  | The hydrogen ends of each water molecule both have a partial positive charge, and therefore would repel each other, making it unlikely that they would be arranged like the picture below shows. p.47,  |
| The fact that water molecules are attracted to each other is an example of ____. | cohesion p.47,  |
| The ability to pour water into a glass past the top of the glass, water forming drops that stick together, and waterbugs not falling through the surface of a pond can be explained by the phenomenon of _____. | cohesion p.47,  |
| The attraction of water molecules to the surfaces of some materials is called _____. | adhesion (Adhesion between water molecules and the glass in the graduated cylinder are responsible for the upward pull of water molecules along the sides, known as a meniscus. Specifically, the glass just above the water line is also attracting water molecules, so the water is pulled upward. This is also how capillary action works.) p.48,  |
The meniscus observed in a graduated cylinder full of water is caused by the ____ of water to the molecules that make up the glass in the cylinder.,  | adhesion p.48,  |
| What are the four emergent properties of water that contribute to Earth's fitness for life? | 1) Cohesion 2) Ability to moderate temperature 3) expansion upon freezing 4) Waters ability as a solvent p.47 |
| The energy of motion is called ____. | kinetic energy p.48 |
| The total amount of kinetic energy due to molecular motion in a body of matter is described as the ___ within that body of matter. | heat p.48 |
| The average kinetic energy of the molecules in a body of matter is measured as _____. | temperature p.48 |
| Pure water freezes at ___ Celsius and boils at ___ Celsius. | 0, 100 p.48 |
| A calorie is the amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of ____ g of water by ____ degree Celsius. | 1,1 p.48 |
| The "calories" on food packages are actually _____. | kilocalories (1000 calories = 1 kilocalorie) p.48 |
| A joule (J) is a measure of ____. | energy p.48 |
| The ____ of a substance is defined as the amount of heat (energy) that must be absorbed or lost by a substance to change its temperature by 1 degree Celsius. | specific heat (In the graph below, it shows that the specific heat is 1cal/C for the liquid phase of water. This is represented by the gentle upwardly sloping part of the graph between 0 and 100C) p.48,  |
| Compared with most other substances, water has an unusually high ____ which explains why it can store a lot of energy and it takes a lot of energy to change its temperature. | specific heat p.48 |
| Why doesn't it get really cold or really hot when you are out at sea? | The high specific heat of water allows it to absorb a lot of heat from the air without increasing its own temperature too much. When cold air blows over the ocean, the large amount of heat (not to be confused with temperature) can be transferred to the air. Since air has a much lower specific heat, it will warm up easily. In places like the Bering Sea of Alaska, the ocean water keeps the air from getting too much below 20 degrees Fahrenheit even in the middle of winter. In summer, it keeps the air from getting too much above 55 degrees F. pp.48&49 |
| The transformation from a liquid to a gas is called ____ or ____. | evaporation or vaporization (boiling is the temperature at which the average molecule has enough energy to overcome the attractions that hold molecules together as a liquid. Therefore, the molecules vaporize quite quickly once the boiling point has been reached) p.49 |
| The _____ is the amount of heat needed to convert 1 gram of a substance already at it's boiling point from a liquid to a gas. | heat of vaporization (Even though a liquid has reached it's boiling point, more energy is needed to break the intermolecular bonds between the molecules so they can separate. In the case of water with it's relatively strong hydrogen bonds giving water molecules strong cohesion, it takes a relatively high heat of vaporization to change liquid into gas. Likewise, when water condenses, a lot of heat is quickly released as those hydrogen bonds reform. That's why you don't want to keep your hand over a steaming pot of water long enough for the water vapor to condense on your skin.) p.49,  |
| 1 calorie of energy must be absorbed by water at 99 Celsius to reach 100 Celsius. How many calories must water at 100 Celsius absorb to reach 101 Celsius? | If you answered 1 calorie, you are wrong. To reach 101 Celsius, water must first be converted from a liquid to a gas. This involves the breaking of hydrogen bonds that hold the water molecules together as a liquid. To break all the hydrogen bonds requires much more energy than it does to simply get the molecules in liquid water to move faster by an average of 1 degree Celsius. This energy requirement is called the heat of vaporization, which is quite high for water compared to most liquids. p.49,  |
| Water helps moderate Earth's temperature by _____ a lot of heat to become water vapor at the equator and then moving toward the poles to ____ that heat as it _____. | absorbing, release, condenses p.49 |
| The _____ of water from humans and other organisms helps keep them cool. | evaporation (or vaporization) p.49 |
| Water reaches its greatest density at ___ degrees Celsius. | 4 pp.49&50,  |
| In a lake during winter, where all the water is close to freezing, where would you find the warmest water? | At the bottom, because water that is colder than 4 Celsius is less dense than water at 4 Celsius. All the water in a lake in winter will be less than 4 Celsius, so the coldest water, being the least dense, rises to the surface. pp.49&50,  |
| In a lake during summer, where would you find the warmest water? | Close to the surface. As long as water is more than 4 Celsius, it behaves like most substances, becoming less dense (and floating) as temperature increases. pp.49&50,  |
| If ice didn't float, lakes and oceans would ______. | eventually freeze solid because ice would sink, exposing liquid water to cold winter temperatures instead of insulating it from the cold temperatures. p.50 |
| A(n) ______ solution is a solution in which water is the solvent. | aqueous p.50 |
| The type of substances that dissolve best in water are ____. | ionic substances and polar covalent substances p.51 |
| Any substance that is attracted to water is said to be ____. | hydrophilic (hydro = water, philic = loving) p.51 |
| Any substance that is repelled by water is said to be ____. | hydrophobic (hydro = water, phobic = fearing) p.51 |
| A mixture of liquid with a substance that remains suspended in the liquid (instead of dissolving) is called a(n) ____. | colloid p.51 |
| 1 mole of a substance is equal to ____ particles of that substance | 6.02 X 10 ^23 (6.02 times ten to the twenty third power) pp.51&52 |
| How would you go about making a 2 molar solution of glucose? | Add 2 moles of glucose to about 1/2 a liter of water. Stir it until it is completely dissolved, then add more water until you have exactly 1 liter of solution. Molarity is defined as the number of moles per liter of solution. Therefore, you would need to figure out the mass of one mole of glucose (by adding up the atomic masses of 6 carbon, 12 hydrogen, and 6 oxygen atoms), multiplying that by two to get 2 moles, massing it out on a balance and dissolving it in water as described in the first sentence. p.52 |
Which type of bond is represented by the dotted line? By the straight line inside the water molecule?,  | Dotted lines = hydrogen bonds, straight lines = covalent bonds p.47,  |
The picture below shows water dissociating into ___ and ___ ions., 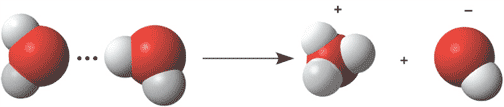 | hydronium and hydroxide ions p.53,  |
| If the concentration of hydrogen (hydronium) ions in a solution is higher than the concentration of hydroxide ions, the solution will be ____. | acidic p.53 |
The substance shown below is a(n) ____ and an increase in its concentration will cause a(n) ___ in pH.,  | hydrogen ion, drop in pH (to become more acidic) p.53,  |
The substance shown below is a(n) ____ and an increase in its concentration will cause a(n) ___ in pH.,  | hydronium ion, drop in pH (to become more acidic) p.53,  |
The substance shown below is a(n) ____ and an increase in its concentration will cause a(n) ___ in pH.,  | hydroxide ion, increase in pH (to become more basic) p.53 |
.,  | strong acids p.53,  |
.,  | strong bases p.53 |
.,  | weak acids p.53,  |
.,  | weak bases p.53,  |
| The pH scale is kind of like the richter scale (for earthquakes) in that a change of one (such as going from pH 4 to pH 3) represents a ___-fold change. | 10-fold change (for example, pH 3 is 10 times more acidic than pH 4) pp.53&54 |
| _____ are substances that minimize (or dampen) changes in pH. | Buffers p.54 |
| _____ work by accepting hydrogen ions from the solution when they are in excess and donating hydrogen ions to the solution when they have been depleted. They usually contain a _____ and its corresponding ____. | Buffers, weak acid, base p.54 |
| Acid precipitation refers to rain, snow, or fog with a pH less than ____. | 5.2 (uncontaminated rain has a pH of 5.6 due to carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mixing with it on its way down to form carbonic acid) pp.55&56 |
| The binding together of like molecules, often by hydrogen bonds, is called ____. | cohesion p.47,  |
| A common measure of solute concentration, referring to the number of moles of solute per liter of solution is called ___. | molarity p.52 |
The sphere of water molecules around each dissolved ion is called a(n) ___.,  | hydration shell p.50,  |
| The property of a liquid whereby the surface becomes cooler during evaporation, due to the loss of highly kinetic molecules to the gaseous state, is called ____. | evaporative cooling p.49 |
| A substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is called a(n) ___. | base p.53 |
| A water molecule that has lost a proton is called a(n) ____. | hydroxide ion (remember, a proton is the same thing as a hydrogen ion because hydrogen normally has one proton, 1 electron and no neutrons, so when it becomes a positively charged ion by losing an electron, all that is left is a single proton) pp.52&53 |
| The attraction between DIFFERENT kinds of substances is called ____. | adhesion (Adhesion between water molecules and the glass in the graduated cylinder are responsible for the upward pull of water molecules along the sides, known as a meniscus. Specifically, the glass just above the water line is also attracting water molecules, so the water is pulled upward. This is also how capillary action works.) p.48,  |
| A measure of how difficult it is to break or stretch the surface of a liquid is called ___. | surface tension (This is responsible for the ability of the water strider in the picture below to stay on the surface of the water) p.48,  |
| The pH of a solution with a hydronium ion concentration of 1 X 10^-7 (one times 10 to the negative seven) moles per liter is _____. | 7 (remember, pH is equal to the negative log of the hydronium ion concentration) pp.53&54 |
| The pH of a solution with a hydronium ion concentration of 1 X 10^-3 (one times 10 to the negative three) moles per liter is _____. | 3 (remember, pH is equal to the negative log of the hydronium ion concentration) pp.53&54 |
| The pH of a solution with a hydronium ion concentration of 1 X 10^-14 (one times 10 to the negative fourteen) moles per liter is _____. | 14 (remember, pH is equal to the negative log of the hydronium ion concentration) pp.53&54 |
| The pH of a solution with a hydronium ion concentration of 1 mole per liter is ____. | Zero (1 mole per liter can also be expressed as 1 X 10^0, because 10 to the zero power = 1. When you express the hydonium ion concentration in scientific notation, as long as the it is 1 X 10^-n, the pH will be n) pp.53&54 |
| What is the average body temperature of humans in degrees Celsius? | 37 p.48 |
| Which type of weak acid acts as a buffer to keep the pH of your blood from changing too much? | carbonic acid (Look at the equations at the bottom of the picture below. In your blood, there is a mixture of carbonic acid it's two decomposition products, the hydrogen ion and the bicarbonate ion. If some new acid is added to blood, the new hydrogen ions will react with bicarbonate ions to form carbonic acid. That keeps the hydrogen ion concentration from going up too much and keeps the pH from dropping too much. If a base is added to blood, the extra hydroxide ions can either react with undissolved carbon dioxide to form the bicarbonate ion, or they can react with the hydrogen ions to form water. The removal of the hydrogen ions would cause more carbonic acid to decompose, increasing the hydrogen ion concentration to offset the effects of adding the base to the blood) p.54,  |
| Higher concentrations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causes the pH of ocean water to ___ as more carbon dioxide is dissolving into the water. This is making it harder for some ocean organisms like hard corals and animals with shells to build their skeletons and shells because carbonate ions dissolved in the water are reacting with the new hydrogen ions being introduced instead of with calcium that is used to make _______, the main ingredient in the shells and coral skeletons. | drop, calcium carbonate (CaCO3) p.55 |
| How do you calculate the molarity of a solution? | Divide the moles of solute by the volume of the entire solution measured in liters. p.52 |
| What does the root word "kilo-" mean? | kilo- = a thousand (kilocalorie: a thousand calories) |
| What does the root word "philic-" mean? | loving (Philia means loving. Hydro means water. Hydrophilic means water loving) |
| What does the root word "phobic-" mean? | fearing (Phobia means fear. Hydro means water. Hydrophobic means water fearing) |