| A | B |
|---|
| What are the building blocks of all matter? | atoms p. 33 |
| The nucleus of an atom is made up of ____ and ____ | protons and neutrons p. 33 |
| Electrons have a ___ charge | negative p. 33 |
| Protons have a ___ charge | positive p. 33 |
| Neutrons have a ___ charge | neutral (no) charge p. 33 |
| Which type of sub-atomic particle orbits the nucleus? | electrons p. 33 |
| Positive charges are attracted to ____ charges | negative p. 33 |
| Positive charges are repelled by ____ charges. | positive p. 33 |
| Negative charges are repelled by ____ charges | negative p. 33 |
| An electron would be attracted to which type of sub-atomic particle? | proton p. 33 |
| The center region of an atom is called a(n) ____. | atomic nucleus p. 33 |
| All of the elements are listed in the ____. | periodic table p. 36 and appendix B |
| The ____ is equal to the number of protons in an atom. | atomic number p. 33 |
| The number of protons + the number of neutrons is equal to the ____ | mass number p. 33 |
| The mass number is equal to the | number of protons and neutrons p. 33 |
| The atomic number is equal to the number of ____ in an atom | protons p. 33 |
| The number below the chemical symbol on the periodic table that usually has a few decimal places is known as the ____. | average atomic mass p. 34 |
| If an element has a mass # of 23 and an atomic # of 11, how many protons will it have? Neutrons? | 11 protons and 12 neutrons p. 33 |
| Two or more different elements bond together to form ____. | compounds p. 31 |
| A compound held together by covalent bonds is called a(n) ___. | molecule p. 38 |
| Atoms or molecules that become charged because they gain or lose electrons are called ___. | ions p. 40 |
| A negatively charged ion would be ____ by another negatively charged ion. | repelled p. 40 |
| A positively charged ion would be ____ by another positively charged ion. | repelled p. 40 |
| A negatively charged ion would be ___ by a positively charged ion. | attracted p. 40 |
| Matter is _____. | Anything that takes up space and has mass. p. 31 |
| _____ is anything that takes up space and has mass. | Matter p. 31 |
| A(n) ______ is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. | element p. 31 |
| A compound in which atoms are joined together by ionic bonds is called a(n) ___. | ionic compound p. 40 |
| A(n) ___ is the smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element. | atom p. G3 |
| The tiny bits of matter that make up an atom are called ___. | sub-atomic particles p. 33 |
| Isotopes of a certain element have the same number of ____ but differ in the number of _____. | protons, neutrons p. 34 |
| Elements that differ from each other because of the number neutrons, but not protons, are called ____. | isotopes p. 34 |
| _____ is defined as the capacity to cause change. | Energy p. 35 |
| In _____ bonds, pairs of electrons are shared between two or more atoms. | covalent p. 38 |
| Bonds in which electrons aren't shared at all (because one atom has a MUCH higher electronegativity than the other) are called ______. | ionic bonds p. 40 |
| A charged atom, (or molecule) is called a(n) ___. | ion p. 40 |
| Compounds formed by ionic bonds are called ____ . | ionic compounds p. 40 |
| The most important characteristic about a biological molecule is its ____. | shape p. 42 |
In the chemical reaction picture below, the molecules on the left side of arrow are called the ____ while the molecules on the right side of the arrow are called the ____., 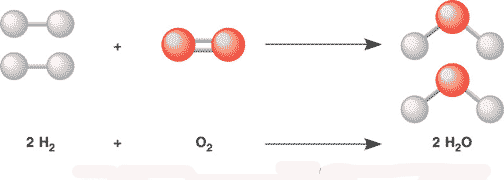 | reactants, products (notice how there are the same number of each type of atom on both sides of this balanced chemical reaction),  |