| A | B |
|---|
| A liquid that has a uniform mixture of two or more substances is know as a(n) ___. | solution p.50 |
| In a glass of salt water, the ___ would be the solvent. | water p.50 |
| In a glass of salt water, the ___ would be the solute. | salt p.50 |
| In a solution of sugar and water, the sugar would be the ___. | solute p.50 |
| In a solution of sugar and water, the water would be the _____. | solvent p.50 |
| Acidic solutions have a pH that is ____ seven. | below pp.53&54 |
| Basic solutions have a pH that is ___ seven. | above pp.53&54 |
| Distilled water has a pH of ___. | seven pp.53&54 |
| A liquid with a pH of 1 would be described as being ___ than a liquid with a pH of 5. | more acidic pp.53&54 |
| A liquid with a pH of 6 would be described as being ___ than a liquid with a pH of 2 | less acidic pp.53&54 |
| A liquid with a pH of 8 would be described as being ___ than a liquid with a pH of 14. | less basic pp.53&54 |
| A liquid with a pH of 13 would be described as being ___ than a liquid with a pH of 7.8. | more basic pp.53&54 |
| As temperature ____, particles move faster and faster | increases p.48 |
| As temperature ____ particles move slower and slower. | decreases p.48 |
| Bonds in which the electrons between two atoms are shared about equally (because both atoms have similar electronegativities) are called _____. | nonpolar covalent bonds p.39 |
| Bonds in which the electrons between two atoms are not SHARED equally (because one atom has a significantly higher electronegativity) are called _____. | polar covalent bond p.46 |
| Bonds in which electrons aren't shared at all (because one atom has a MUCH higher electronegativity than the other) are called ______. | ionic bonds p. 40 |
| A weak attraction between hydrogen in one molecule and either an oxygen or nitrogen atom in another molecule is called a(n) _____. | hydrogen bond p.40 |
| Molecules in which the overall charge is unequally distributed, leading to parts of the molecule having a partial positive charge while other parts have a partial negative charge (like water) are called ______. | polar molecules p.46 |
| The fact that water molecules are attracted to each other is an example of ____. | cohesion p.47,  |
| The ability to pour water into a glass past the top of the glass, water forming drops that stick together, and waterbugs not falling through the surface of a pond can be explained by the phenomenon of _____. | cohesion p.47,  |
| The attraction of water molecules to the surfaces of some materials is called _____. | adhesion (Adhesion between water molecules and the glass in the graduated cylinder are responsible for the upward pull of water molecules along the sides, known as a meniscus. Specifically, the glass just above the water line is also attracting water molecules, so the water is pulled upward. This is also how capillary action works.) p.48,  |
The meniscus observed in a graduated cylinder full of water is caused by the ____ of water to the molecules that make up the glass in the cylinder.,  | adhesion p.48,  |
| Pure water freezes at ___ Celsius and boils at ___ Celsius. | 0, 100 p.48 |
| The transformation from a liquid to a gas is called ____ or ____. | evaporation or vaporization (boiling is the temperature at which the average molecule has enough energy to overcome the attractions that hold molecules together as a liquid. Therefore, the molecules vaporize quite quickly once the boiling point has been reached) p.49 |
| The _____ of water from humans and other organisms helps keep them cool. | evaporation (or vaporization) p.49 |
| Water reaches its greatest density at ___ degrees Celsius. | 4 pp.49&50,  |
| If ice didn't float, lakes and oceans would ______. | eventually freeze solid because ice would sink, exposing liquid water to cold winter temperatures instead of insulating it from the cold temperatures. p.50 |
| 1 mole of a substance is equal to ____ particles of that substance | 6.02 X 10 ^23 (6.02 times ten to the twenty third power) pp.51&52 |
Which type of bond is represented by the dotted line? By the straight line inside the water molecule?,  | Dotted lines = hydrogen bonds, straight lines = covalent bonds p.47,  |
The picture below shows water dissociating into ___ and ___ ions., 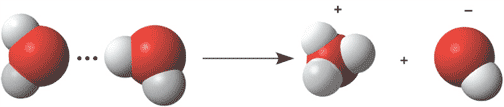 | hydronium and hydroxide ions p.53,  |
| If the concentration of hydrogen (hydronium) ions in a solution is higher than the concentration of hydroxide ions, the solution will be ____. | acidic p.53 |
The substance shown below is a(n) ____ and an increase in its concentration will cause a(n) ___ in pH.,  | hydrogen ion, drop in pH (to become more acidic) p.53,  |
The substance shown below is a(n) ____ and an increase in its concentration will cause a(n) ___ in pH.,  | hydronium ion, drop in pH (to become more acidic) p.53,  |
The substance shown below is a(n) ____ and an increase in its concentration will cause a(n) ___ in pH.,  | hydroxide ion, increase in pH (to become more basic) p.53 |
.,  | strong acids p.53,  |
.,  | strong bases p.53 |
.,  | weak acids p.53,  |
.,  | weak bases p.53,  |
| The pH scale is kind of like the richter scale (for earthquakes) in that a change of one (such as going from pH 4 to pH 3) represents a ___-fold change. | 10-fold change (for example, pH 3 is 10 times more acidic than pH 4) pp.53&54 |
| _____ are substances that minimize (or dampen) changes in pH. | Buffers p.54 |
| The binding together of like molecules, often by hydrogen bonds, is called ____. | cohesion p.47,  |
| A common measure of solute concentration, referring to the number of moles of solute per liter of solution is called ___. | molarity p.52 |
| A substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is called a(n) ___. | base p.53 |
| The attraction between DIFFERENT kinds of substances is called ____. | adhesion (Adhesion between water molecules and the glass in the graduated cylinder are responsible for the upward pull of water molecules along the sides, known as a meniscus. Specifically, the glass just above the water line is also attracting water molecules, so the water is pulled upward. This is also how capillary action works.) p.48,  |
| A measure of how difficult it is to break or stretch the surface of a liquid is called ___. | surface tension (This is responsible for the ability of the water strider in the picture below to stay on the surface of the water) p.48,  |