| A | B |
|---|
What type of molecule is this?, 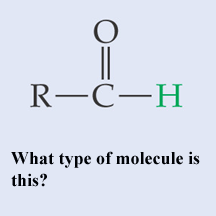 | A basic aldehyde pp64&65,  |
What type of molecule is this?,  | carboxylic-acid pp64&65,  |
What type of molecule is this?, -copy.gif) | aldehyde (hexanal) pp64&65, -copy.gif) |
What type of molecule is this?, .gif) | ketone (2-butanone) pp64&65, .gif) |
What type of molecule is this?, 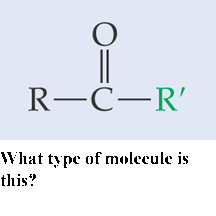 | Ketone pp64&65, 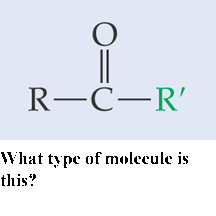 |
| What is the molecular formula and shape of benzene? | C6H6, ring p61 |
| One of several organic compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures, and therefore, different properties. | isomer p62 |
| A functional group present in organic acids consisting of a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group. | carboxyl group pp64&65,  |
| A functional group consisting of a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom (--SH). | sulfhydryl group pp64&65,  |
| A functional group that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. It can act as a base in a solution, accepting a hydrogen ion and acquiring a charge of +1. | amino group pp64&65, 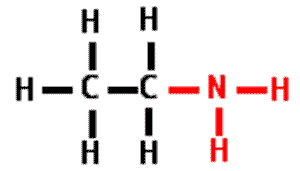 |
| An organic molecule consisting only of carbon and hydrogen is called a(n) _____. | hydrocarbon (the butane molecule below is a hydrocarbon because it has only hydrogens and carbons) p61, 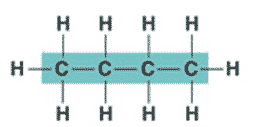 |
| An arrangement of two non-carbon atoms, each bound to one of the carbons in a carbon-carbon double bond,where the two non-carbon atoms are on the same side relative to the double bond. | cis p62, 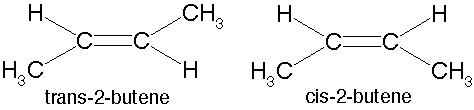 |
| An arrangement of two non-carbon atoms, each bound to one of the carbons in a carbon-carbon double bond,where the two non carbon atoms are opposite sides relative to the double bond. | trans p62, 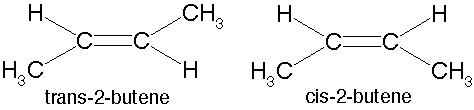 |
| A specific configuration of atoms commonly attached to the carbon skeleton of organic molecules and usually involved in chemical reactions. | functional group (the carboxyl-group in red below is a functional group that makes the molecule acidic because it often loses the hydrogen as a hydrogen ion into the solution which lowers the pH of the solution) p63,  |
| A type of isomer in which carbons have covalent bonds to the same atoms, but these atoms differ in their spatial arrangements due to the inflexibility of carbon-carbon double bonds. | Cis-trans isomers (a.k.a. geometric isomer) p62, 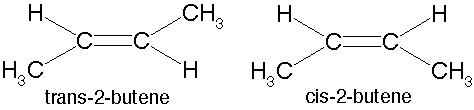 |
| A functional group that is important in energy transfer. | Phosphate group (think of ATP-->ADP + P + energy) p66, 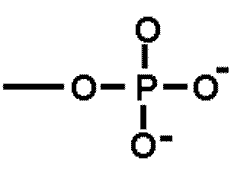 |
| One of several organic compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the covalent arrangement of their atoms. | structural isomer p62, 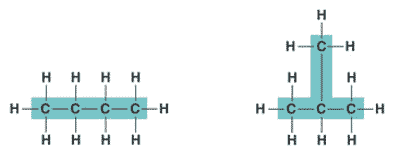 |
| A functional group present in aldehydes and ketones that consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom. | carbonyl group pp64&65, 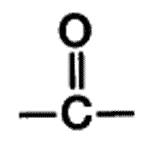 |
| A functional group consisting of a hydrogen atom joined to an oxygen atom by a polar covalent bond. Molecules possessing this group are soluble in water and are called alcohols. | hydroxyl group pp64&65,  |
| One of two molecules that are mirror images of each other. | enantiomer (also called a stereo-isomer) p62, 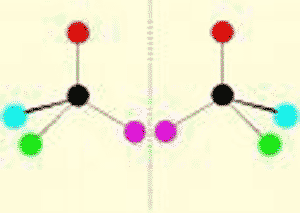 |
What type of molecule is this?,  | An aldehyde (It's an aldehyde because the carbonyl group is coming off a terminal carbon. If it wasn't, it would be a ketone. The name of this molecule is ethanal, since it has two carbons like ethane) pp64&65,  |
What is the name of the functional group in red?,  | amino group pp64&65,  |
What is the name of this functional group?,  | carbonyl group pp64&65,  |
What is the name of this type of molecule and what is the name of its functional group?, 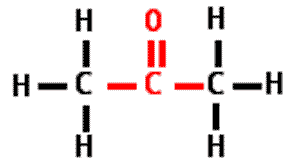 | ketone, carbonyl group (The specific name of the molecule pictured is propanone because it is a ketone with 3 carbons like propane) pp64&65,  |
What is the name of this type of molecule and what is the name of its functional group?,  | Carboxylic acid, carboxyl group (This molecule is called ethanoic acid but is more commonly referred to as acetic acid which is the acid in vineger) pp64&65,  |
What is the name of this molecule?, 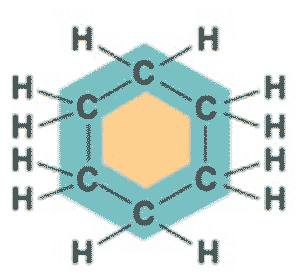 | cyclohexane p61,  |
What do we call these two molecules?,  | enantiomers (or stereoisomers; notice that they are mirror images of each other) p62,  |
What type of isomers are these?, 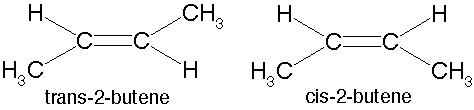 | cis-trans isomers (a.k.a. geometric isomers) p62, 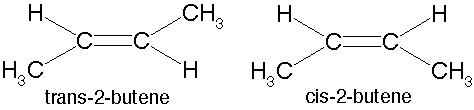 |
Which of these cis-trans isomers would be considered the "cis" isomer and which would be the "trans" isomer?,  | The one on the left is "cis" and the one on the right is "trans" (the prefix trans means across) p62,  |
What is the name of this type of molecule and what is the name of its functional group?,  | An alcohol, hydroxyl group (This is ethanol because it has two carbons like ethane. The common name is ethyl alcohol) p64&65,  |
What is the name of this functional group?,  | phosphate group p64&65,  |
What type of isomers are these?,  | structural isomers p62,  |
What is the name of this functional group?,  | Sulfhydryl group p64&65,  |
| Carbon can form a wide variety of compounds because it forms ____ covalent bonds. | 4 (p60) |
Each line in a structural formula (like the one below) represents a _____., 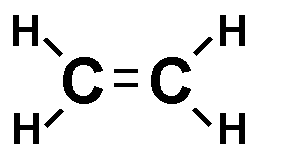 | pair of shared electrons, 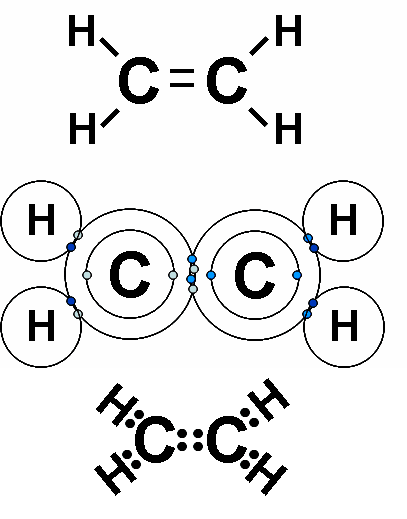 |
| ____ is the source of carbon for all of the organic molecules found in organisms. | carbon dioxide p58 |
| An important energy storing molecule that has 3 phosphate groups is called _____. | Adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP) p66, 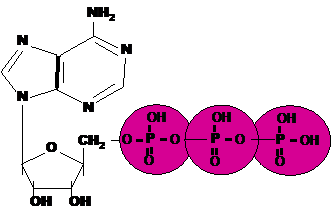 |
| Hydrocarbons can be either _____, _____, or _____ shaped. | straight, branched, or ring shaped p61 |
| Organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen are called ______. | hydrocarbons p61 |