| A | B |
|---|
| typography | the art of making fonts |
| font | characters that are used in writing |
| Oldstyle | category of font with angle serifs, light thick/thin transition and angled stress,  |
| Modern | category of font with thin flat serifs and dramatic vertical thick/thick transition,  |
| Sans Serif | category of font with no serifs and no thick/thin transition,  |
| Slab Serif | category of font with thick serifs but no thick/thin transition,  |
| Script | category of font that looks like handwriting,  |
| ascenders | parts of letters that go higher than the x-height, 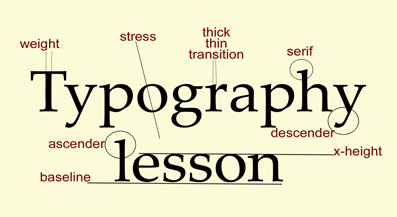 |
| descenders | parts of letters that drop down below the baseline,  |
| baseline | the invisible line that most of the letters sit on,  |
| serifs | little flairs at the ends of characters,  |
| Decorative | often include symbols or flairs that convey specific information or emotions,  |
| weight | thickness of the line in a character,  |
| 6 categories of fonts | Oldstyle, Modern, Sans Serif, Slab Serif, Decorative, and Script,  |
| x-height | the invisible light that is the top of most lower case letters,  |
| stress | the angle when you connect the thinnest parts of a letter together,  |
| thick/thin transition | the difference in some letters and fonts between the thickest part of a letter to the thinnest part,  |
| Example of Oldstyle | Times New Roman, 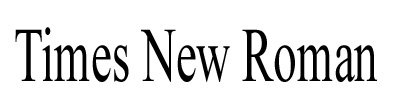 |
| Example of Modern | Bernard or Bodini, 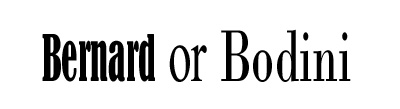 |
| Example of Sans Serif | Helvetica, Arial, Calibri,  |
| Example of Slab Serif | Rockwell, 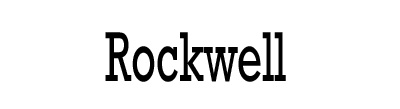 |
| Example of Decorative | WingDings, Castellar or Betsy Flannagan, 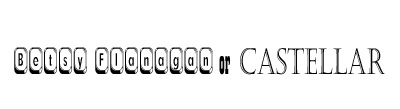 |
| Example of Script | Palace Script, Rage Italic, 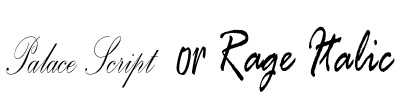 |
| "Sans" is Latin for | without or none, i.e. Sans Serif means without serifs |