| A | B |
|---|
base, 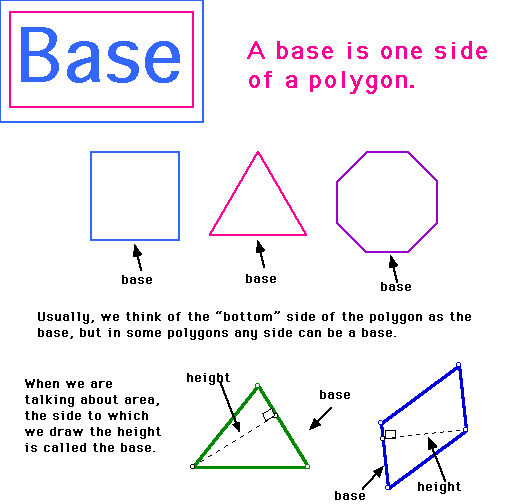 | A number that is raised to a power. For example, in 5³, the base is 5 |
| dividend | The number in division that is being divided. In 35 ÷ 7 = 5, the dividend is 35. |
| divisor | The number that divides another number. For example, in 35 ÷ 5 = 7, the divisor is 5. |
| expanded notation | A way of writing a number as the sum of the values of each digit. For example, in expanded notation, 356 is written as 300 + 50 + 6. |
| exponent | A small raised number used in exponential notation to tell how many times the base is used as a factor. For example, in 5³, the exponent is 3. |
| exponential notation | A way to show repeated multiplication by the same factor. For example, 2³ is exponential notation for 2 * 2 * 2. |
| factor | each of the 2 or more numbers in a product |
| number-and-word notation | A way of writing a number using a combination of numbers and words. Example, 27 billion is number-and-word notation for 27,000,000,000. |
partial-quotients method, 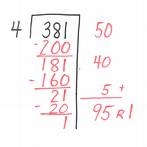 | a way to divide in which the dividend is divided in a series of steps. |
| power of 10 | A whole number that can be written as a product of 10’s example, 100 is equal to 10 *10, or 102 |
| precise | Exact or accurate. The smaller the unit or fraction of a unit used in measuring, the more precise the measurement is. |
| quotient | The result of dividing one number by another number. Example: in 35 ÷ 5 = 7, the quotient is 7. |
| remainder | An amount left over when one number is divided by another number. |
| scientific notation | A system for writing numbers in which a number is written as the product of a power of 10 and a number that is at least 1 and less than 10. Example 4 * 1012 is scientific notation for 4,000,000,000,000. |
| standard notation | The most familiar way of representing whole numbers, integers, and decimals. Example, standard notation for three hundred fifty-six is 356. |
| truncate | In a decimal, two cut off all digits after the decimal point, or after a particular place to the right of the decimal point. Also called rounding down |