| A | B |
|---|
What does "A" in this graph represent?,  | Energy of activation without an enzyme present p153,  |
What does "B" in this graph represent?,  | The lowered energy of activation due to an enzyme being present p153,  |
What does "C" in this graph represent?,  | The change in free energy (∆G) for this reaction, which would be negative, indicating an exergonic reaction p153,  |
What is the green molecule called?, 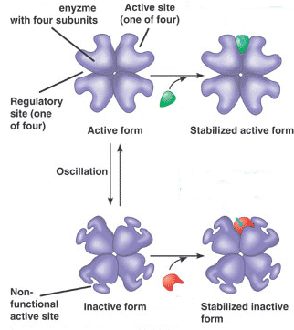 | an allosteric activator p158,  |
What is the red molecule called?,  | an allosteric inhibitor (could also be called a non-competitive inhibitor) p158,  |
What is the name of this molecule and which part of it does "A" represent?,  | "A" represents the three phosphate groups in ATP p149,  |
What is the name of this molecule and which part of it does "B" represent?,  | "B" represents the ribose sugar in ATP p149,  |
What is the name of this molecule and which part of it does "C" represent?,  | "C" represents the adenine (a nitrogenous base) in ATP p149,  |
What concept is this diagram showing and what does the blue molecule represent?,  | competitive inhibition, competitive inhibitor p156,  |
What concept is being shown in this diagram?, 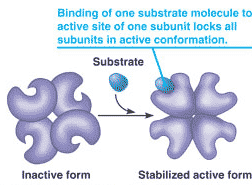 | cooperativity p158,  |
The graph below represents a(n) ____ reaction,  | endergonic (notice the positive ∆G) p147,  |
The graph below shows the change in free energy for a(n) _____ reaction.,  | endergonic p147,  |
The change in free energy is ____ for this reaction.,  | positive p147,  |
The letter "A" represents a(n) ____ for this enzyme.,  | active site p154,  |
The letter "B" represents a(n) ____.,  | enzyme p154,  |
The letter "C" represents a(n) ____.,  | substrate p154,  |
The graph below represents a(n) ____ reaction,  | exergonic (notice the negative ∆G) p147,  |
The graph below shows the change in free energy for a(n) _____ reaction., 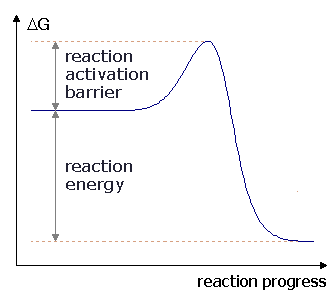 | exergonic p153,  |
The change in free energy is ____ for this reaction.,  | negative p153,  |
The molecules labeled "A" are known as the _____.,  | reactants p152,  |
The molecules labeled "B" are in the _____ state.,  | transition state p152,  |
The molecules labeled "C" are known as the _____.,  | products p152,  |
The arrow labeled "D" shows the ______.,  | change in free energy (∆G) for the reaction (which is negative indicating an exergonic reaction) p152,  |
The difference in free energy between A and B is called the ____.,  | energy of activation p152,  |
This diagram shows a type of metabolic regulation called _____. It's also an example of negative feedback in general because the accumulation of too much product will slow down the creation of more product as a means of maintaining homeostasis.,  | feedback inhibition p160,  |
Which molecule acts as the inhibitor in this diagram and what kind of inhibitor is it?,  | isoleucine acts as an allosteric inhibitor (could also be called a non-competitive inhibitor) p160,  |
This diagram represents the concept of a(n) _______., 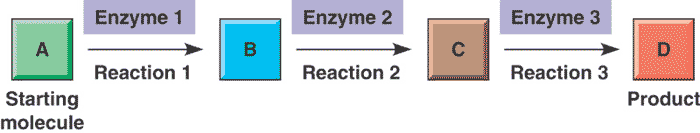 | metabolic pathway (Involves multistep processes to go from the reactant to the final product. Each step is regulated by a different enzyme. "B" and "C" are intermediary products) p142,  |
This diagram shows _____ inhibition. The red molecule is a(n) _______ inhibitor.,  | both blanks in this question could be correctly filled with either the word "allosteric" or the word "non-competitive p156&158,  |
| A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by entering the active site in place of the substrate whose structure it mimics is called a(n) ______. | competitive inhibitor p156 |
| Any non-protein molecule or ion that is required for the proper functioning of an enzyme is called a(n) _____. | cofactor p156 |
| The reactant on which an enzyme works is called the _____. | substrate p153 |
| ______ energy is energy stored by matter as a result of location or spatial arrangement. | Potential energy p143 |
| A macromolecule serving as a catalyst is called a(n) ____. | enzyme (the type of macromolecule that acts as an enzyme is almost always a protein. Sometimes the nucleic acid RNA can act as an enzyme) p152 |
| Any substance, organic or inorganic, that speeds up the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction is called a(n) _____. | catalyst p152 |
| Another word for thermal energy is ____. | heat p143 |
| Another word for heat is ____. | thermal energy p143 |
| An organic cofactor is called a(n) _____. | coenzyme p156 |
| Most vitamins serve as ____ in important metabolic reactions. | coenzymes p156 |
| The specific portion of an enzyme that attaches to the substrate by means of weak chemical bonds is called _____. | the active site p154 |
| A metabolic pathway that synthesizes a complex molecule from simpler compounds is called a(n) ______ pathway. | anabolic p143 |
| A series of chemical reactions that either builds a complex molecule (anabolic pathway) or breaks down a complex molecule into simpler molecules (catabolic pathway) is called a(n) _______ | metabolic pathway p142 |
| The change in shape of the active site of an enzyme that occurs as the substrate enters the active site, allowing it to bind more snugly to the substrate, is referred to as _____. | induced fit p154 |
| A metabolic pathway that releases energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds is called a(n) _____. | catabolic pathway p143 |
| The concept of _________ involves the binding of one substrate molecule to the active site of an enzyme that has several other active sites. | cooperativity p158&159,  |
| The study of energy transformations that occur in a collection of matter is called ____. | thermodynamics p144 |
| A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by binding to a location remote from the active site, changing its conformation so that it no longer binds to the substrate is called a(n) ____ or a(n) ________. | non-competitive inhibitor or allosteric inhibitor p156 & p158 |
| An adenine-containing nucleoside triphosphate that releases free energy when its phosphate bonds are hydrolyzed. This energy is used to drive endergonic reactions in cells. | ATP (adenosine triphosphate) p149 |
| A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s). | enzyme-substrate complex p153 |
| The amount of energy that reactants must absorb before a chemical reaction will start. | activation energy (or energy of activation) p152 |
| A type of regulation that involves the binding of a molecule to a protein that affects the function of the protein at a different site. | allosteric regulation p158 |
| A spontaneous chemical reaction, in which there is a net release of free energy. | exergonic reaction p147 |
| The energy of motion, which is exponentially related to the speed of that motion is called ____ energy. Moving matter does work by imparting motion to other matter. | kinetic energy p143 |
| A quantitative measure of disorder or randomness is called ____. | entropy (the greater the entropy, the greater the disorder) p145 |
| The symbol for entropy is ___. | S p146 |
| The principle of conservation of energy which states that energy can be transferred and transformed, but it can't be created or destroyed. | first law of thermodynamics p144 |
| The potential energy stored in molecules available for release in chemical reactions is called ____. | chemical energy p143 |
| A method of metabolic control in which the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway. | feedback inhibition p160 |
| The principle whereby every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe. Ordered forms of energy are at least partly converted to heat, and in spontaneous reactions, the free energy of the system also decreases. | second law of thermodynamics p145 |
| In cellular metabolism, the use of energy released from an exergonic reaction to drive an endergonic reaction | energy coupling (the reactions would be called coupled reactions) p149 |
| A non-spontaneous chemical reaction, in which free energy is absorbed from the surrounding. | endergonic reaction p148 |
| The total amount of kinetic energy due to molecular motion in a body of matter. | heat p143 |
| The average kinetic energy of a body of matter. | temperature (Temperature is related, but not the same as heat. As an example, a rock that has been "heated up" to lets say, 100C, would have more thermal energy, or heat, than the air in a container the same size as the rock, even if that air was much "hotter," like say, 200C. Heat is the "total" amount of kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. There are many more particles packed into the rock than in the gasses that make up the hot air in the container that has the same volume as the rock. If you wanted the temperature of a small cold room to increase, you would be better off bringing the rock into the room, than the small amount of really hot air, even though the molecules of air are moving at an overall faster average speed, and therefore have a higher average kinetic energy (a.k.a. - temperature) (G-34) |
| The portion of a system's energy that can perform work when temperature and pressure are uniform throughout the system is called ___. | free energy p146 |
| To calculate whether a reaction will be spontaneous or not, you need to calculate the ______ using the equation ______ | The potential change in Gibb's free energy using the equation ∆G= ∆H- T∆S where ∆H is the change in enthalpy, T is temperature in degrees Kelvin and ∆S is the change in entropy p146 |
| A positive ∆H means that a reaction will be ____. | endothermic (Endothermic is slightly different than endergonic. Endothermic reactions require more heat energy than they give off and are usually also endergonic, meaning not spontaneous. However , if you have ever used one of those chemical cold packs, you have witnessed an example of an exergonic "spontaneous" reaction that is very endothermic. This reaction basically uses heat energy from its surroundings, and therefore causes the temperature of the surroundings to drop. To be exergonic "spontaneous" like it is, the reaction must significantly increase the entropy "disorder" of the overall system, leading to a positive delta S that when multiplied by the negative T in the equation ∆G= ∆H- T∆S overcomes the positive delta H to make delta G negative. A negative delta G means the reaction is exergonic "spontaneous." Notice that T (temperature in Kelvin) plays a part in the calculation. If the temperature is not high enough, the overall reaction will be less negative if there is a positive delta S (more disorder) and the product of negative T and delta S may no longer be able to overcome the positive delta H of the ice pack example, and therefore not have a negative delta G. Therefore, there is a point where temperature is too low for ice packs to work. But if its that cold, you might be able to just use snow anyway. ** You won't find this explained in the book, and yes, it is complicated. Give yourself a pat on the back if you understood all that. |
| A negative ∆H means that a reaction will be ____. | exothermic (Meaning heat is released. Also means enthalpy decreases. Enthalpy is the systems total energy, or heat) p146 |
| A positive ∆G means that a reaction will be ____ and _____. | endergonic and non-spontaneous p146 |
| A negative ∆G means that a reaction will be ____ and ______. | exergonic and spontaneous p146 |
| A positive ∆S means that ____. | The products of the reaction are more disordered (have higher entropy) than the reactants |
| A negative ∆S means that ____. | The products of the reaction are more ordered (have lower entropy) than the reactants. |
| When energy stored in certain organic molecules is converted to light (like the glow of a firefly), the process is called _____. | bioluminescence p142 |
| The sum of all of an organism's chemical reactions is called ______. | metabolism p142 |
| Another word for catabolic pathway is _____. | breakdown pathway p143 |
| Another word for anabolic pathway is _____. | biosynthetic pathway p143 |
| Another word for breakdown pathway is _____. | catabolic pathway p143 |
| Another word for biosynthetic pathway is _____. | anabolic pathway p143 |
| The study of how energy flows through living organisms is called _____. | bioenergetics p143 |
| What is the definition of energy? | the capacity to cause change p143 |
| A system that is not able to exchange matter and energy with its surroundings is called a(n) _______ or _______ system. | closed, isolated (The book gives a thermos bottle as an example, but technically, this is not correct because heat energy will be slowly exchanged with the outside of the thermos. There is no such thing as a perfect insulator. Technically, the only truly closed system is the universe as a whole.) p144 |
| A system that is able to exchange matter and energy with its surroundings is called a(n) _______ system. | open p144 |
| For a semi-closed system, what can and can't be exchanged with the surroundings? | energy can, matter can't (see your chapter 8 section 1 notes) |
| A consequence of the second law of thermodynamics is that every energy transformation results in a loss of "useable" energy as some energy in the energy transformations is lost as _____. | heat (The energy is not really lost, it just becomes for all practical purposes "unuseable." The total amount of energy remains the same and therefore does not violate the first law of thermodynamics, that energy can't be created or destroyed.) p144 & 145 |
| True or False: Breaking bonds releases energy. | False (Breaking bonds always requires energy. The formation of bonds releases energy) p148 |
| What are the three types of work that cells do? | chemical, transport, mechanical p149 |
| Building up larger molecules like polymers which require energy for endergonic reactions is an example of cells performing ____ work. | chemical p149 |
| Pumping substances across a cell membrane from areas of low concentration of the substance to areas on the other side of the membrane with already higher concentrations of the substance requires ________ and is an example of a cell performing ______ work. | energy, transport p149 |
| The beating of cilia (tiny hairlike appendages found in some single-celled organisms) or the contraction of muscle cells are examples of cells doing _____ work. | mechanical p149,  |
| It's a fact that the breakdown of sucrose (table sugar) is an exergonic reaction and is therefore spontaneous. Does that mean that sucrose breaks down into glucose and fructose monomers quickly? | No (A spontaneous reaction is not necessarily a quick reaction. A sugar solution, like Mountain Dew, would take years for the sugar to react and break down on it's own. Most exergonic reactions in your body require a catalyst for the reactions to occur quickly enough to be useful. It's a good thing that all of the possible exergonic spontaneous reactions in our body don't happen quickly on their own because otherwise, we would spontaneously combust) p152 |
| Any substance that helps speed up a chemical reaction without being changed permanently itself is called a(n) _____. | catalyst (Remember, the term enzyme only applies to organic catalysts). p152 |
| An organic catalyst is known as a(n) _____. | enzyme p152 |
| At high substrate concentrations, when the enzymes are catalyzing one reaction after another as fast as possible and the only way to speed up the reaction is to add more enzyme, the enzymes already there are said to be _____. | saturated p155 |
| In an enzyme catalyzed reaction in which the enzymes are saturated, what is the only way to speed up the reaction? | Add more enzymes to increase the enzyme concentration (Raising the temperature won't work because substrate molecules are immediately being replaced by new substrate molecules when an enzyme is saturated. In fact, raising the temperature my slow the reaction down if it causes distortions or denaturation of the active site) p155 |
| A site on an enzyme that is not the active site, but can bind inhibitor or activator molecules to change the shape of the active site is known as a(n) _______ or a(n) ________. | regulatory site, allosteric site p158 |
| The concept of cooperativity involves the binding of one _____________ to the ______ site of an enzyme that has several other active sites. When the first substrate molecule binds to an active site, the other active sites change shape to become active also. | substrate molecule, active site p158&159,  |
| A(n) ______ is a series of enzymes attached to a membrane in a manner that facilitates the movement of the product of one enzyme to the next enzyme in the series where the product of the first enzyme becomes the substrate for this next enzyme, almost like a factory assembly line | multienzyme complex p160 |
| A molecule that has a phosphate group temporarily attached to it is a molecule that is said to have been ______. The phosphate group makes the original molecule more reactive (ie gives it more free energy, usually from the coupled reaction of the hydrolysis of ATP), so this process is often times an intermediary step in a multistep reaction that is endergonic overall and wouldn't happen without the step where binding of a phosphate group occurs. | phosphorylated p151 |