| A | B |
|---|
What does "A" in this graph represent?,  | Energy of activation without an enzyme present p153,  |
What does "B" in this graph represent?,  | The lowered energy of activation due to an enzyme being present p153,  |
What does "C" in this graph represent?,  | The change in free energy (∆G) for this reaction, which would be negative, indicating an exergonic reaction p153,  |
What is the name of this molecule and which part of it does "A" represent?,  | "A" represents the three phosphate groups in ATP p149,  |
The graph below represents a(n) ____ reaction,  | endergonic (notice the positive ∆G) p147,  |
The graph below shows the change in free energy for a(n) _____ reaction.,  | endergonic p147,  |
The change in free energy is ____ for this reaction.,  | positive p147,  |
The letter "A" represents a(n) ____ for this enzyme.,  | active site p154,  |
The letter "B" represents a(n) ____.,  | enzyme p154,  |
The letter "C" represents a(n) ____.,  | substrate p154,  |
The graph below represents a(n) ____ reaction,  | exergonic (notice the negative ∆G) p147,  |
The graph below shows the change in free energy for a(n) _____ reaction., 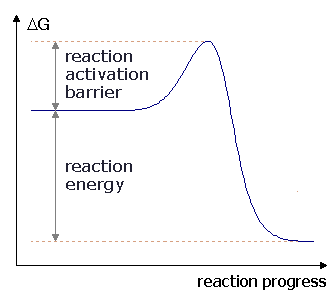 | exergonic p153,  |
The molecules labeled "A" are known as the _____.,  | reactants p152,  |
The molecules labeled "C" are known as the _____.,  | products p152,  |
The arrow labeled "D" shows the ______.,  | change in free energy (∆G) for the reaction (which is negative indicating an exergonic reaction) p152,  |
The difference in free energy between A and B is called the ____.,  | activation energy (a.k.a. energy of activation) p152,  |
| The reactant on which an enzyme works is called the _____. | substrate p153 |
| ______ energy is energy stored by matter as a result of location or spatial arrangement. | Potential energy p143 |
| A macromolecule serving as a catalyst is called a(n) ____. | enzyme (the type of macromolecule that acts as an enzyme is almost always a protein. Sometimes the nucleic acid RNA can act as an enzyme) p152 |
| Any substance, organic or inorganic, that speeds up the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction is called a(n) _____. | catalyst p152 |
| The specific portion of an enzyme that attaches to the substrate by means of weak chemical bonds is called _____. | the active site p154 |
| The amount of energy that reactants must absorb before a chemical reaction will start. | activation energy (or energy of activation) p152 |
| A spontaneous chemical reaction, in which there is a net release of free energy. | exergonic reaction p147 |
| The energy of motion, which is exponentially related to the speed of that motion is called ____ energy. Moving matter does work by imparting motion to other matter. | kinetic energy p143 |
| A quantitative measure of disorder or randomness is called ____. | entropy (the greater the entropy, the greater the disorder) p145 |
| The principle of conservation of energy which states that energy can be transferred and transformed, but it can't be created or destroyed. | first law of thermodynamics p144 |
| The potential energy stored in molecules available for release in chemical reactions is called ____. | chemical energy p143 |
| The principle whereby every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe. Ordered forms of energy are at least partly converted to heat, and in spontaneous reactions, the free energy of the system also decreases. | second law of thermodynamics p145 |
| A non-spontaneous chemical reaction, in which free energy is absorbed from the surrounding. | endergonic reaction p148 |
| The average kinetic energy of a body of matter. | temperature (Temperature is related, but not the same as heat. As an example, a rock that has been "heated up" to lets say, 100C, would have more thermal energy, or heat, than the air in a container the same size as the rock, even if that air was much "hotter," like say, 200C. Heat is the "total" amount of kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. There are many more particles packed into the rock than in the gasses that make up the hot air in the container that has the same volume as the rock. If you wanted the temperature of a small cold room to increase, you would be better off bringing the rock into the room, than the small amount of really hot air, even though the molecules of air are moving at an overall faster average speed, and therefore have a higher average kinetic energy (a.k.a. - temperature) (G-34) |
| The sum of all of an organism's chemical reactions is called ______. | metabolism p142 |
| True or False: Breaking bonds releases energy. | False (Breaking bonds always requires energy. The formation of bonds releases energy) p148 |
| It's a fact that the breakdown of sucrose (table sugar) is an exergonic reaction and is therefore spontaneous. Does that mean that sucrose breaks down into glucose and fructose monomers quickly? | No (A spontaneous reaction is not necessarily a quick reaction. A sugar solution, like Mountain Dew, would take years for the sugar to react and break down on it's own. Most exergonic reactions in your body require a catalyst for the reactions to occur quickly enough to be useful. It's a good thing that all of the possible exergonic spontaneous reactions in our body don't happen quickly on their own because otherwise, we would spontaneously combust) p152 |
| An organic catalyst is known as a(n) _____. | enzyme p152 |