| A | B |
|---|
| The movement of water molecules across a cell membrane is called ___. | osmosis p.133 |
| In a salt water solution, the salt is known as the ___. | solute p.50 |
| If a cell membrane allows glucose to pass through it, then the cell membrane is said to be ____ to glucose. | permeable p.131, 
|
| In a salt water solution, the water is known as the ____. | solvent p.50 |
| The movement of particles across a cell membrane from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration is known as ____. | diffusion (The definition of diffusion can also be applied to particles just spreading out evenly in space if there is no membrane involved) p.132,  |
| The cell membrane is said to be _______ permeable to substances because it lets some pass through but not others. | selectively p.125 |
| The type of substances that can most easily diffuse across a cell membrane are ____ substances. | small non-polar substances p.131 |
| The composition of nearly all cell membranes is a double-layered sheet called a __________ | lipid bilayer pp.125-127 |
| Charged particles usually pass through _____ to get into cells. | channel proteins p.134 |
| Cells will shrink if placed into a _____ solution. | hypertonic pp.133&134 |
| When energy is needed to force molecules across a cell membrane, _______ is taking place. | active transport p.135,  |
| Cells will grow bigger if placed in a ____ solution. | hypotonic p.135 |
When osmotic pressure increases in plant cells, why don't the cells usually burst?, 
| Plant cells have a tough cell wall that keeps the cell from expanding enough to burst. p.134 |
| If a solution is 6% solutes, it will be ____ % water. | 94 (see your notes) |
| If a solution is 90% water, it will have ___ % solutes. | 10 (see your notes) |
| A solution that has the same concentration of solutes as the interior of a cell is known to be ____. | isotonic p.133 |
| Active transport requires _____. | energy p.135 |
| If a substance is diffusing across a cell membrane, it is going from an area of ____ concentration to an area of ___ concentration. | high, low p.132 |
When osmotic pressure decreases in a plant, the ______ shrinks and the plant ____., 
| central vacuole, wilts (see your notes) |
| When osmotic pressure increases in plants, the ______ gets bigger and the plant ___. | central vacuole, gets turgid/stiff (see your notes) |
The elodea cells in this picture are surrounded by a ______ solution.,  | hypotonic p.134,  |
The process pictured below is called ____., 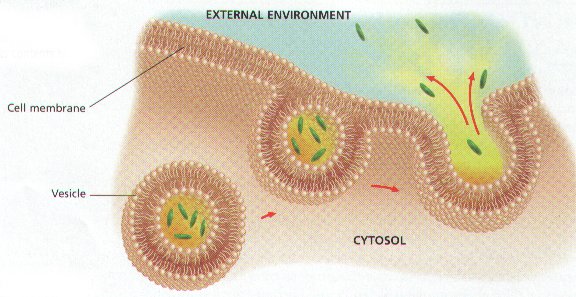 | exocytosis p.138,  , , 
|
The elodea cells pictured below have been soaking in a ____ solution.,  | hypertonic,  |
The process pictured below is called ____., 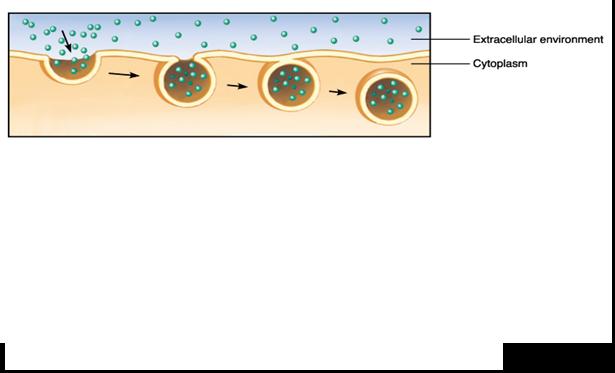 | endocytosis pp.138&139,  , , 
|
| The type of endocytosis that takes in solid particles (usually food) is called ____. | phagocytosis pp.138&139 |
| The type of endocytosis that takes in liquids is called ___. | pinocytosis pp.138&139 |
| The type of endocyctosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes is called _____. | pinocytosis pp.138&139 |
| ______ is the cellular uptake of macromolecules and particulate substances by localized regions of the plasma membrane that surround the substance and pinch off to form intracellular vesicles. | endocytosis pp.138&139,  |
| In comparing two solutions, the one with the greater solute concentration is called the _____ solution. | hypertonic p.133 |
| _______ transport involves the diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane. | Passive transport p.133 |
| Passive transport involves the ______ of a substance across a biological membrane. | diffusion p.133 |
| The cellular secretion of macromolecules by the fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane. | exocytosis pp.138&139,  |
| _______ involves the movement of a substance across a biological membrane against its concentration or electrochemical gradient with the help of energy input and specific transport proteins. | Active transport p.135,  |
| A(n) ______ protein is typically a transmembrane protein with hydrophobic regions that completely span the hydrophobic interior of the membrane. | integral protein (Remember from chapter 6 that they talked about integrins. Integrins are a type of integral protein that is attached to cytoplasmic microfilaments that the integrin can move, or tug on, when a ligand binds to the receptor part of the integrin on the outside of the cell. This allows communication from outside the cell to change something going on inside the cell) p.129, 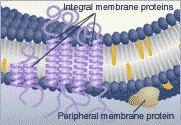 |
| A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule is called a(n) _____. | ligand p.138 |
| A molecule that has both a hydrophobic region and a hydrophilic region is described as being _____. | amphipathic p.125 |
| A channel protein in a cell membrane that allows passage of a specific ion down its concentration gradient is called a(n) _____. | ion channel p.135 |
| A property of biological membranes that allows some substances to cross more easily than others is called _____. | selective permeability p.125 |
| In comparing two solutions, the one with the lower solute concentration is called the _____ solution. | hypotonic p.134 |
| The currently accepted model of cell membrane structure, which envisions the membrane as a collage of individually inserted protein molecules drifting laterally in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids, is called _____. | the fluid mosaic model pp.125-126, 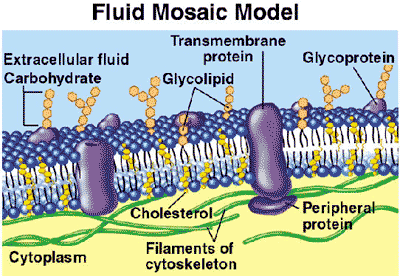 |
| A(n) ______ is a protein structure that involves active transport by using ATP to force hydrogen ions out of a cell, generating a membrane potential in the process. | proton pump (remember, a hydrogen ion is a proton) p.137, 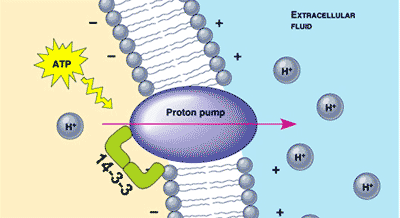 |
| A carbohydrate covalently attached to a lipid is called a(n) _____. | glycolipid (think of glycogen, which is a carbohydrate, attached to a lipid) p.130 |
| Another word to describe plants which are very firm due to the cells of the plant having a greater solute concentration than their surroundings is _____. | turgid p.134 |
| A special transport protein in the plasma membrane of animal cells that transports sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell against their concentration gradients is called _____. | a sodium-potassium pump p.137, 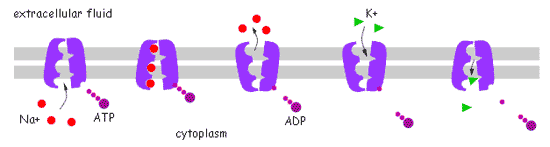 |
| The movement of specific molecules into a cell by the inward budding of membanous vesicles containing proteins with receptor sites specific to the molecules being taken in; enables a cell to acquire bulk quantities of specific substances. | receptor-mediated endocytosis pp.138&139, 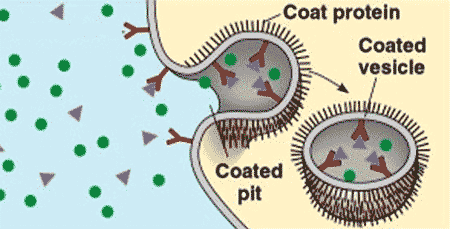 |
| The charge difference between a cell's cytoplasm and the extracellular fluid, due to a buildup of cations or anions on one side of the membrane. | membrane potential p.136 |
| A carbohydrate covalently attached to a protein is called a(n) _____. | a glycoprotein p.130, 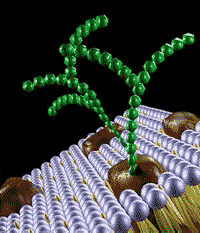 |
| The combination of forces caused by an imbalance of both the concentration of an ion and the imbalance of charge caused by the ion imbalance is called a(n) _____ gradient. | electrochemical gradient p.137,  |
| The coupling of the downhill diffusion of one substance to the uphill transport of another against its own concentration or electrochemical gradient. | cotransport p.137 |
| A channel protein in a cell membrane that opens or closes in response to a particular stimulus. | gated channel p.135, 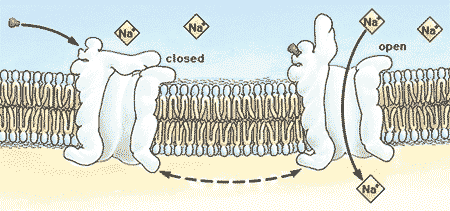 |
| The regulation of solute and water concentrations. | osmoregulation p.134 |
| A transport protein in the plasma membrane of a plant or animal cell that specifically facilitates the diffusion of water across the membrane (osmosis). | aquaporin p.132, 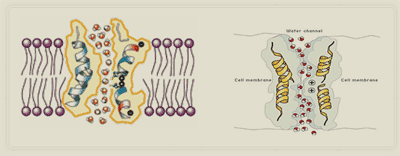 |
| An ion transport protein that generates voltage across a membrane. | electrogenic pump (A proton pump is a specific type of electrogenic pump because it only pumps hydrogen ions, a.k.a. protons) p.137 |
| A(n) ______ protein is a transmembrane protein that helps a certain substance or class of closely related substances to cross the membrane. | transport protein p.131 |
| Cells will have to use active transport if they are trying to transport substances against the ________ of that substance. | concentration gradient p.135 |
| A protein appendage loosely bound to the surface of a membrane and not embedded in the lipid bilayer. | peripheral protein p.129,  |
| ______ occurs in walled cells when the cytoplasm shrivels and the plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall (due to the cell losing water to a hypertonic environment). | plasmolysis (This term applies to plant, bacterial, and fungal cells. The term to describe shriveling of un-walled animal cells would be "crenation." The opposite of crenation, in which an un-walled cell bursts due to over-expansion is called "cytolysis.") p.134, 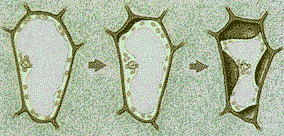 |
| A measure of the ability of a solution to cause a cell within it to gain or lose water is called _____. | tonicity p.133 |
| _______ diffusion is the spontaneous passage of molecules and ions, bound to specific carrier proteins, across a biological membrane down their concentration gradients. | Facilitated diffusion p.134,  |
The picture below is showing _____ transport.,  | active transport p.135,  |
Which of the six major functions of cellular proteins is being shown below?, 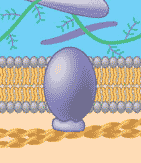 | attachment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix p.129,  |
Which of the six major functions of cellular proteins is being shown below?,  | cell-cell recognition p.129,  |
Which of the six major functions of cellular proteins is being shown below?, 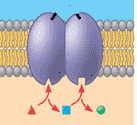 | enzymatic activity (enzymes that are involved in multistep metabolic pathways are often found near each other embedded in a membrane) p.129,  |
Which process is shown below?,  | Simple diffusion p.132,  |
Which process is shown below?,  | facilitated diffusion (It's diffusion because the particles are travelling down the concentration gradient. It's facilitated because a channel protein is helping) p.134,  |
What type of membrane protein is shown below (be specific)?,  | gated channel protein p.135,  |
What are the brown and green things below?,  | glycoproteins p.127,  |
Which of the six major functions of cellular proteins is being shown below?, 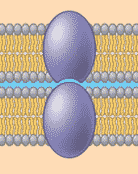 | intercellular joining (for example, tight junctions, and gap junctions) p.129,  |
The cell on the right has undergone _____.,  | plasmolysis p.134,  |
The proton pump below is being used to set up a(n) ________ gradient.,  | electrochemical gradient p.137,  |
What type of endocytosis is shown below?,  | Receptor-mediated endocytosis pp.138&139,  |
Which of the six major functions of cellular proteins is being shown below?, 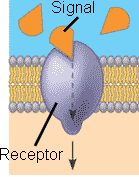 | signal transduction p.129,  |
What is the specific name of the cell membrane protein in the picture below?,  | sodium-potassium pump (very important in nerve cells) pp.136&137,  |
Which of the six major functions of cellular proteins is being shown below?, 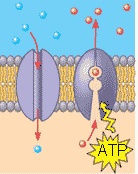 | transport p.129,  |
Which type of transport protein is pictured below?, 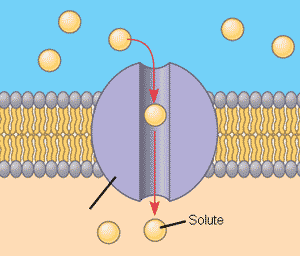 | channel protein p.131, 134&135,  |
Which type of transport protein is pictured below?,  | carrier protein p.132, 134&135,  |
What type of solution was the cell on the left exposed to?,  | hypotonic p.134,  |
What type of solution was the cell on the middle exposed to?,  | isotonic pp.133&134,  |
What type of solution was the cell on the right exposed to?,  | hypertonic pp.133&134,  |
Which process is shown below?, 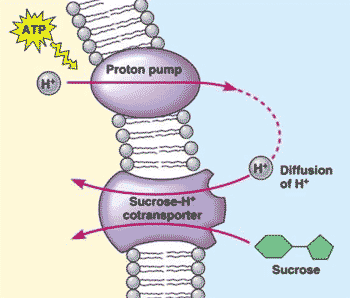 | cotransport p.137,  |
| The most abundant lipids in most membranes are ______. | phospholipids p.125 |
| ______ is simply the diffusion of water molecules from one side of a cell membrane to the other. | Osmosis p.133 |
| Osmosis is simply the _____ of water molecules from one side of a cell membrane to the other. | diffusion p.133 |
Why do paramecia, like the one pictured below, have contractile vacuoles that pump water out of the cell?,  | They live in fresh water which is hypotonic to the cell. If they didn't, they would take in too much water and burst. (notice the contractile vacuole in the micrograph below) p.134,  |
| The pressure applied to the inside of a plant cell wall by the cell itself trying to expand due to water intake in hypotonic environments is called _____ pressure | turgor pressure p.134 |
| Plants or plant cells that are very firm due to the pressure applied to the inside of the cell wall from water uptake within the cell itself are said to be _____. | turgid p.134 |
| Plants or plant cells that are limp or wilted due to the loss of pressure to the inside of the cell wall from too little water uptake within the cell itself are said to be _____. | flaccid p.134 |
| An animal cell that bursts due to excessive water uptake in hypotonic environments is said to have been ____. | lysed p.134,  |
| Cells with a separation of opposite charge by their cell membrane are said to have _____ potential. This is due to the storage of ______ energy, a.k.a. ______. | membrane potential, electric potential energy, voltage (Similar to a battery that has positive and negative charge separated. The flow of electrons from one side to the other through a wire allows the electric potential energy to be extracted while the battery slowly drains until the charge reaches equilibrium and the battery goes dead) p.136 |