| A | B |
|---|
| The number of chromosomes in a gamete is represented by the letter ___. | n p251 |
| A carrot has a diploid number of 18. What is it's haploid number? | 9 p251 |
| Gametes are normally produced by the process of ___. | meiosis pp251&252, 
|
| Another word for sex or reproductive cell is ___. | gamete p249 |
| What are the two main types of gametes? | sperm and egg p249 |
| During which stage of meiosis do chromosomes undergo synapsis to pair up and connect with each other? | prophase I (Below is a pair of homologous chromosomes, loosely attached to each other. Each chromosome is duplicated as a pair of sister chromatids. This formation is often times called a tetrad) p254, 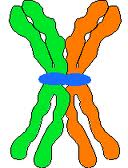 |
| During which stage of meiosis do homologous chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell? | metaphase I p254 |
| During which stage of meiosis do sister chromatids separate from each other? | anaphase II p255 |
| What happens between meiosis I and meiosis II that reduces the number of chromosomes? | DNA replication does not occur but cytokinesis does. pp253-255 |
| When does DNA replication occur during meiosis? | Interphase I only (remember, there is no interphase II) p253 |
| What is the diploid number of chromosomes in humans? | 46 (also written as 2n=46) p251 |
| What is the haploid number for humans? | 23 (also written as n=23) p251 |
| The gametes of fruit flies have 4 chromosomes each. What is the diploid number of chromosomes for fruit flies? | 8 (remember the diploid number is always twice the haploid number) p251 |
| _________ chromosomes are chromosomes that have the same types of genes, but are not identical. | Homologous (They are not identical because one came from the mother and the other from the father) p250, 
|
| _________ are chromosomes that have the same types of genes, and are identical. | Sister chromatids p253 |
| A(n) _____ is a segment of DNA that has the instructions for making one protein. | gene p249 |
| When two homologous chromosomes are lined up right next to each other during meiosis, they are referred to as a(n) ___. | tetrad (This term is not used in your book, but it is a very commonly used term, so I want you to know it) |
| An organism's gametes have ___ the number of chromosomes as are found in the organism's body cells. | half p251 |
| During which stage of meiosis might crossing over occur? | prophase I pp254&258 |
| When homologous chromosomes are lined up next to each other during meiosis, they might swap pieces of DNA. This phenomenon is called ___. | crossing over pp254&258 |
| Crossing over during meiosis is important because it increases ___. | genetic variation (= the number of different chromosomes, and therefore different combinations of traits, that offspring can inherit) p258 |
Which diagram is mitosis and which is meiosis?,  | Mitosis is on the left and meiosis is on the right. p256,  |
When chromosomes are lined up like this during meiosis, what are they referred to as?, 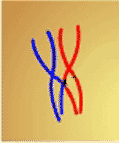 | A tetrad (This is not in your book, but it is a very commonly used term, so know it),  |
Which process from meiosis is shown below and during which stage would it occur?, 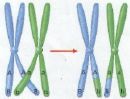 | The picture shows "crossing over" and it usually happens during prophase I. pp258&259,  |
| The transmission of traits from one generation to the next is called _______ or ________. | inheritance or heredity p248 |
| The scientific study of heredity is called ______. | genetics p248 |
| The fusion of sperm and egg is called _____. | fertilization pp248&251 |
| Segments of DNA that act as hereditary units are called ____. | genes p249 |
| Reproductive cells are called _____. | gametes (they are also called sex cells or reproductive cells and include the egg and sperm) p249 |
| The DNA of eukaryotes is subdivided into _____ within the nucleus of the cell. | chromosomes p249 |
| Most human cells have ____ chromosomes. | 46 p249 |
| How many DNA molecules make up a chromosome? | 1 p.249 |
| One chromosome includes several hundred to a few thousand _____, each of which is a specific sequence of nucleotides within the DNA molecule. | genes p249 |
| A gene's specific location along the length of a chromosome is called the gene's _____. | locus p249 |
| Single-celled eukaryotic organisms can reproduce asexually by _____ cell division. | mitotic p249 |
| In ______ reproduction, a single individual is the sole parent and passes identical copies of all its genes to its offspring. | asexual p249 |
| An individual that reproduces asexually gives rise to a(n) ______, which is a genetically identical individual. | clone p249 |
| In ________ reproduction, two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combinations of _____ inherited from the two parents. | sexual, genes p249 |
| A(n) _____ is the generation-to-generation sequence of stages in the reproductive history of an organism. | life cycle p250 |
| A(n) _____ cell is any cell other than a gamete. | somatic p249 |
| A picture of all the chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell, arranged side-by-side in homologous pairs is called a(n) _____. | karyotype p250,  |
| Homologous chromosomes can also be referred to as _______. | homologs p250, 
|
| The X and Y chromosomes are referred to as the _______. | sex chromosomes p250 |
| All chromosomes other than the sex chromosomes are called _____. | autosomes p250 |
| When considering a homologous pair of chromosomes, one came from the ____ and the other came from the ____. | father, mother p250 |
| Diploid cells are cells that have ____________. | both pairs of homologous chromosomes p251 |
| Haploid cells are cells that have _____________. | a single chromosome set (not both pairs of a homologous set) p251 |
| A fertilized egg is called a(n) _____. | zygote p251 |
| The type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in half is called _____. | meiosis p252, 
|
| The type of life cycle that involves both diploid and haploid multicellular stages is called ______. | alternation of generations (commonly seen in plants and some species of algae) p252,  |
| In organisms that show an alternation of generations life cycle, the multicellular diploid stage is called the ______ and produces ______ cells called _____ through ______. | sporophyte, haploid cells called spores through meiosis p252,  |
| Spores have a(n) _____ number of chromosomes and become ______. | haploid, multicellular haploid organisms called gametophytes. p252,  |
| A haploid gametophyte makes _____ through ______. | gametes, mitosis p252,  |
| In a life cycle that has alternation of generations, the sporophyte produces the ________ as its offspring. | gametophyte (by first producing the haploid spore that grows into the haploid gametophyte via mitosis) p252,  |
| In a life cycle that has alternation of generations, the gametophyte produces the ________ as its offspring. | the sporophyte (by first producing gametes via mitosis that fuse and grow into diploid sporophytes) p252,  |
| Organisms that have an alternation of generations life cycle have a gametophyte that makes gametes via _____. | mitosis (remember that gametophytes are already haploid) p252,  |
| Sporophytes produce spores via _____. | meiosis (Remember, sporophytes are diploid and spores are haploid. Unlike haploid gametes, spores don't fuse with another cell to become diploid zygotes. They grow mitotically into a haploid multicellular gametophyte that produce haploid gametes by mitosis) p252,  |
| Most fungi and some protists, including some algae have a life cycle in which the ______ stage is only single-celled. | diploid p252,  |
| Most _____ as well as some protists have a multicellular stage that is always haploid (ie - they don't have a diploid multicellular stage). | fungi p252,  |
| The criss-crossed regions of a tetrad are called ______. | chiasmata p254,  |
| The pairing of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I is called _____. | synapsis p254 |
| During _______ of meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate. | Anaphase I p254,  |
| During ____ of meiosis, sister chromatids line up in a straight line. | Metaphase II p255,  |
The picture below is called a(n) ______ .,  | karyotype (These are the chromosomes of a male. You can tell because there is one X and one Y chromosome) p250,  |
| In humans, what type of sex chromosomes do males have? | an X and a Y p250 |
| In humans, what type of sex chromosomes do females have? | two X chromosomes p250 |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?,  | interphase (there is no interphase II so there is no need to say interphase I),  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?,  | prophase I p254,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?, 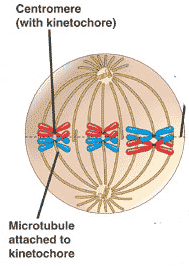 | metaphase I (Homologous chromosomes are lining up to get separated. In metaphase II, sister chromatids are lining up to get separated) p254,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?,  | anaphase I (Notice that homologous chromosomes are separating, but not the attached sister chromatids) p.254,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?, 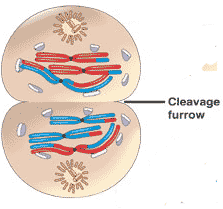 | telophase I p254,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?, 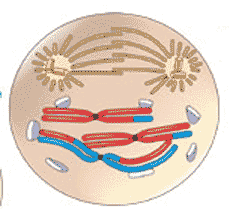 | prophase II p255,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?,  | metaphase II (If it was metaphase I, you would see homologous pairs of duplicated chromosomes, a.k.a., tetrads, lined up) p255,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?,  | anaphase II (If it was anaphase I, you would see homologous chromosomes pulling apart with sister chromatids still stuck together) p255,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?, 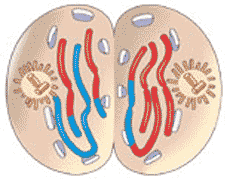 | telophase II (If it was telophase I, you would still see sister chromatids stuck together) p255,  |
| Meiosis results in ___ non-identical daughter cells (looking for a number here) | four p256 |
| During prophase I, homologous chromosomes line up and become physically connected to one another by zipper-like proteins called the _______. | synaptonemal complex p254 |
| The number of possible combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes formed in the gametes during meiosis due to independent assortment can be calculated using the formula _____. | 2 to the nth power where n = the haploid number p258 |
| Individual chromosomes that contain DNA derived from two different parents due to crossing over are called ______. | recombinant chromosomes p258 |
| Specialized diploid cells in the testes and ovaries that divide by meiosis to form gametes (sperm and eggs) are called _______. | germ cells p251 |
| Different versions of the same gene are called _____. | alleles (For instance, one of the chromosomes for humans contains the gene for eye color, but there are two different versions of this gene, the brown allele and the blue allele. A pair of homologous chromosomes might have an allele for brown color on one chromosome while the chromosome that was inherited from the other parent has the allele for blue color. We will learn which of those two alleles gets expressed in chapter 14) p253 |
| What are the three mechanisms that contribute to genetic variation arising from sexual reproduction? | Independent assortment of chromosomes, crossing over, random fertilization p257 |
| One source of genetic variation is due to the fact that the first meiotic division results in each pair of homologous chromosomes splitting up to sort its maternal and paternal homologs independently of every other pair. This phenomenon is called _____. | independent assortment of chromosomes (You get half your chromosomes from your mother and half from your father. When you make your own eggs or sperm, there is a small chance that you could pass on only the chromosomes that you inherited from your father, or only the chromosomes you inherited from your mother. This depends on how they line up during metaphase I. In most cases, you end up passing on a combination of chromosomes from both your mother and father) see the diagram on page 258 |
| In humans, another source of genetic variation arising from sexual reproduction is the fact that each sperm or egg can have at least 8.4 million different combinations of maternal or paternal chromosomes. The fusion of the sperm and egg during fertilization will produce a zygote with any of 70 trillion diploid combinations of chromosomes. This phenomenon that increases genetic variation among humans is called ______. | Random fertilization (This explains why it is basically impossible to inherit all of the same chromosomes as a sibling, especially when you factor in the additional differences in chromosomes caused by crossing over. Only identical twins will inherit identical chromosomes) p258 |
| _____ are the original source of new and different alleles, which are then mixed and matched during meiosis and random fertilization. | Mutations p259 |
| Stable environments favor ____ reproduction. | asexual (If an organism is doing well in its current environment and the environment isn't changing, it's best to reproduce asexually because then you know your genetically identical offspring is also well suited for that environment. Another advantage is that asexual reproduction requires less energy than sexual reproduction. Plus dating, weddings, and kids that require parental care are expensive) p.259 |
| In a changing environment that becomes more difficult to survive, _____ reproduction is favored for organisms that can reproduce either way. | sexual (For a population, the ability to mix and match genes through sexual reproduction gives the population a chance of producing offspring with better combinations of genes to survive the new environment) p259 |
| The root word "homo-" means ___. | like (homologous: like chromosomes that form a pair) |